Editor: Nina
Researchers formulate a hyaluronic acid hydrogel incorporating resveratrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to enhance therapeutic efficacy and provide sustained release for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Key Preview
Research Question
This study investigates the efficacy of a novel hyaluronic acid hydrogel containing resveratrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as an adjuvant in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD).
Research Design and Strategy
The research employs a systematic approach, encompassing the preparation and characterization of nanoparticles, formulation of hydrogels, and evaluation of therapeutic effects in vitro.
Method
The methodology includes the synthesis of chitosan nanoparticles, incorporation into hyaluronic acid hydrogels, and subsequent testing using human keratinocyte cell lines.
Key Results
The findings reveal that the developed hydrogel effectively protects keratinocytes from oxidative damage and significantly reduces the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with AD.
Significance of the Research
This research paves the way for more effective topical treatments for AD, potentially offering a safer alternative to traditional steroidal therapies.
Introduction
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a prevalent chronic inflammatory skin disorder that manifests as intense itching, redness, and skin lesions, significantly impairing the quality of life for affected individuals. Characterized by a compromised skin barrier, AD often results in increased susceptibility to infections and exacerbation due to environmental triggers. It commonly begins in childhood, but its effects can persist into adulthood, necessitating effective long-term management strategies.
Traditionally, the management of AD has relied on topical corticosteroids, which are known for their potent anti-inflammatory properties. These medications are typically applied directly to the affected skin areas to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. While effective, the long-term use of corticosteroids is often limited by their potential side effects, including skin thinning, adrenal suppression, and the risk of developing tolerance, leading to increased dosing and potential systemic effects.
The current approach to treating AD faces distinct challenges, particularly concerning the delivery of therapeutic agents. Traditional drug delivery systems often lead to suboptimal drug absorption, rapid degradation, and insufficient localization at the target site. These limitations can result in inadequate therapeutic outcomes, increased frequency of application, and greater risk of side effects, thereby diminishing patient adherence to treatment regimens.
To address these challenges, innovative drug delivery strategies have emerged, emphasizing the use of nanotechnology to enhance the efficacy and safety of treatments. One promising approach involves the development of biocompatible nanoparticles that can encapsulate therapeutic agents and facilitate their controlled release. This study introduces a novel formulation of hyaluronic acid hydrogel containing resveratrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles, aimed at providing a more effective and safer topical treatment for atopic dermatitis. By leveraging the unique properties of nanoparticles, this innovative delivery system seeks to improve drug bioavailability, enhance therapeutic effects, and mitigate the adverse side effects associated with traditional therapies.
Research Team and Aim
The research team is led by Dr. Raffaele Conte, who conducted this study at the AMES Group Polydiagnostic Center and the Research Institute on Terrestrial Ecosystems (IRET)—CNR. This research was carried out over several months and culminated in the publication of their findings in the paper titled “Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Resveratrol-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as an Adjuvant in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment.” The study was published in January 2023 in the Journal of Functional Biomaterials.
The aim of the research, as stated by Dr. Conte, is to formulate an effective drug delivery system utilizing hyaluronic acid and chitosan nanoparticles to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of resveratrol in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Experimental Process
Primary Technique
The primary technique employed in this study was the synthesis and characterization of resveratrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (Res-NPs) followed by their incorporation into a hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogel (Res@gel). This method leverages the biocompatibility and biodegradability of chitosan and hyaluronic acid, addressing the limitations of traditional drug delivery systems by enhancing the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of resveratrol in the management of atopic dermatitis (AD).
Experiment 1: Synthesis of Chitosan Nanoparticles
Key Steps:
- Chitosan was solubilized in 1% (v/v) lactic acid overnight at room temperature.
- Sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP) and resveratrol were dissolved in ethanol.
- The resveratrol solution was gradually added to the chitosan solution under constant stirring (750 rpm) for 1 hour to promote nanoparticle formation through ionotropic gelation.
- The resulting nanoparticles were collected via centrifugation and washed with distilled water to remove unencapsulated resveratrol.
Data Collection and Analysis:
Particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential were measured using a NanoSight NS300 Nanoparticles Tracking Analysis (NTA). Encapsulation efficiency (EE) was assessed by measuring the residual unencapsulated resveratrol in the supernatant with a spectrophotometer.
Result:
The synthesized Res-NPs exhibited sizes ranging from 120 nm to 500 nm, with an encapsulation efficiency of up to 80%. The zeta potential measurements indicated a positive surface charge, which is essential for cellular uptake.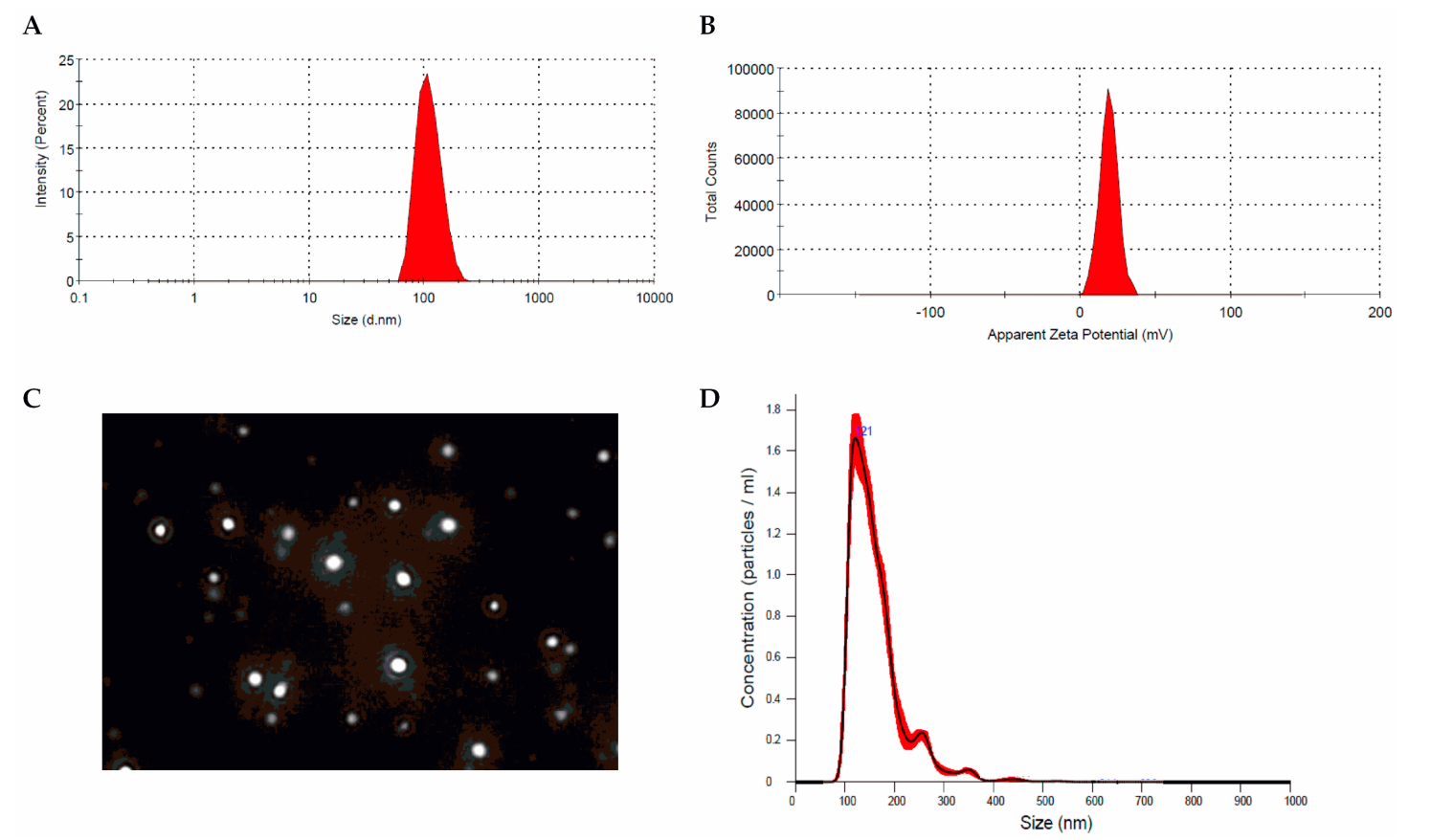
Fiugre. 1 Res-NPs. (A) Size distribution, (B) zeta potential profile, © screenshot of representative NTA video, and (D) NTA measurements for Res-NPs in suspension. Frequency distributions are averages of 3 measurements.
Novel Aspects:
This experiment innovatively utilized the ionotropic gelation method to create chitosan nanoparticles with high encapsulation efficiency, a significant improvement over traditional methods that often yield lower EE.
Experiment 2: Hydrogel Formulation
Key Steps:
- A solution of 200 mg of HA was prepared in 5 mL of double distilled water under stirring for 24 hours.
- The previously synthesized Res-NPs were lyophilized and incorporated into the HA solution at varying concentrations (1%, 5%, and 10% w/w).
- The mixture was stirred for an additional hour at 4 °C to ensure homogeneity.
Data Collection and Analysis:
The hydrogels were characterized for their swelling ratio and rheological properties using a HAAKE Rheo Stress 6000 rheometer. The stability of the hydrogel was evaluated by monitoring changes in viscosity and appearance over time.
Result:
The resulting Res@gel formulations demonstrated a smooth and homogeneous consistency, with enhanced viscosity and viscoelastic properties compared to the HA hydrogel alone, indicating successful incorporation of nanoparticles.
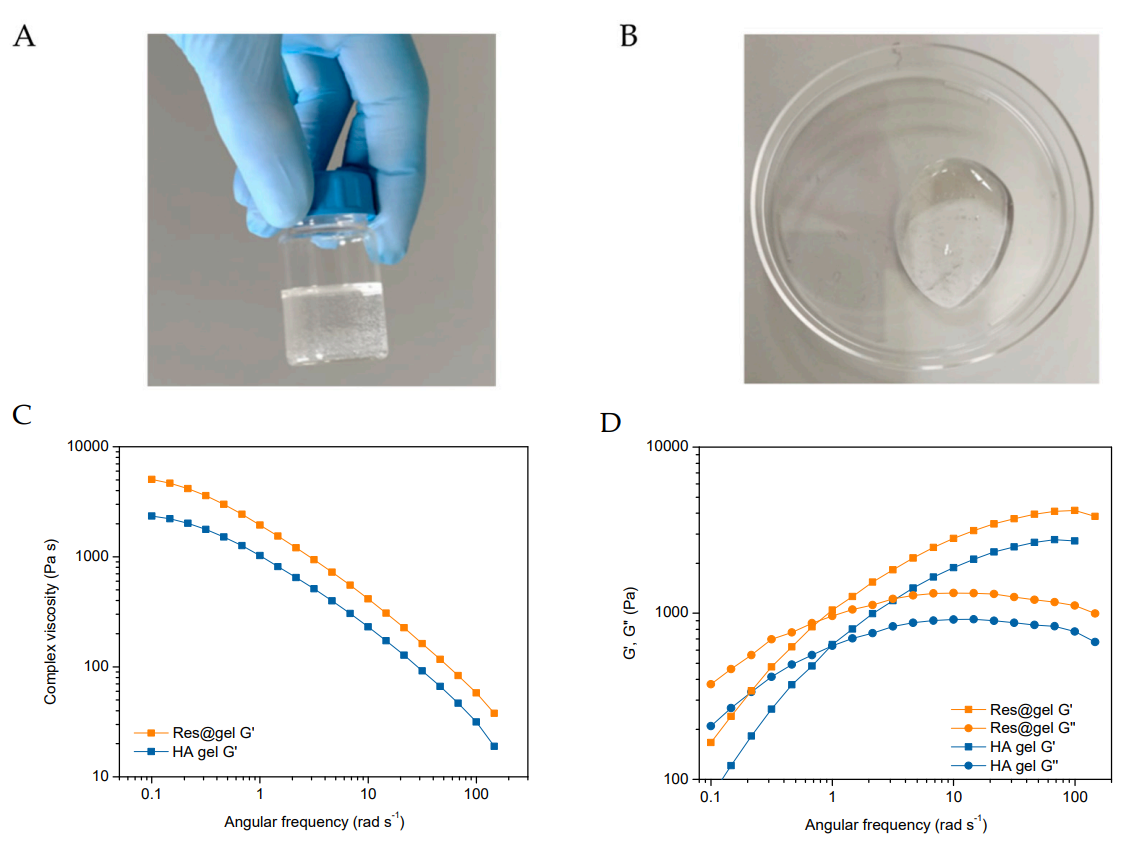
Figure. 2 appearance and rheological properties of the HA-based hydrogels. (A,B) Representative images of Res@gel10. Dependence of © viscosity and (D) viscoelastic on the angular frequency of HA and Res@gel10.
Novel Aspects:
The incorporation of Res-NPs into HA hydrogels represents an advanced drug delivery system that improves the mechanical properties and drug retention, overcoming the rapid degradation often seen in standard hydrogel formulations.
Experiment 3: In Vitro Testing on Human Keratinocytes
Key Steps:
- HaCaT cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) supplemented with fetal bovine serum and antibiotics.
- Cells were treated with Res@gel formulations for 24 hours, followed by stimulation with TNF-α (10 ng/mL) and IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) for 24 hours to simulate atopic dermatitis conditions.
- Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were measured using dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) as a fluorescent probe.
Data Collection and Analysis:
Fluorescent intensity was quantified using a microplate reader, and the cytokine secretion was assessed through enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to evaluate mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Result:
Res@gel pre-treatment significantly reduced ROS levels by approximately 1.5-fold compared to TNF-α/IFN-γ-treated cells. Additionally, it inhibited the secretion and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-4, IL-6, and IL-13.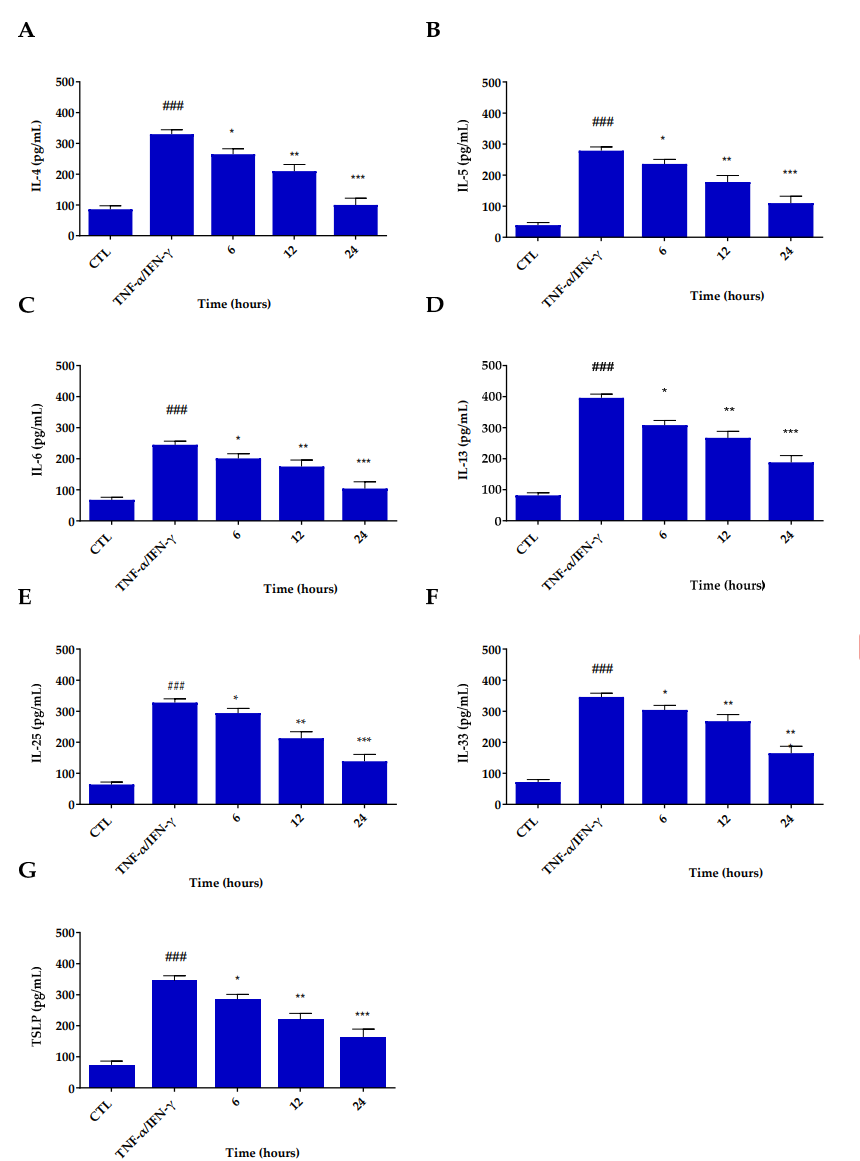
Figure. 3 Inhibitory effects of Res@gel10 on inflammatory cytokine secretion in TNF-α/INF-γ-induced HaCaT cells. Secretion of IL-4 (A), IL-5 (B), IL-6 ©, IL-13 (D), IL-25 (E), IL-33 (F), and TSLP (G) was measured by ELISA assay. Cells were pre-treated with Res@gel10 for 24 h, then stimulated with TNF-α/IFN-γ for 24 h. Results are expressed as the mean of three independent experiments ± S.D (n = 3). ### p < 0.001 TNF-α/IFN-γ-treated cell.
Novel Aspects:
The study introduces a dual-action approach by not only delivering resveratrol through a hydrogel but also enhancing its therapeutic effects through sustained release, which is a marked improvement over conventional topical treatments that often lack such efficacy
Conclusion
The successful development of this innovative drug delivery system was achieved through the meticulous formulation of resveratrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles embedded in a hyaluronic acid hydrogel. This approach effectively addressed the limitations of traditional therapies by enhancing drug bioavailability and providing a sustained release profile.
The study highlights that the synthesized Res@gel not only protects human keratinocytes from oxidative stress but also significantly reduces the secretion and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with atopic dermatitis. By demonstrating good biocompatibility and a favorable therapeutic profile, this research presents a promising alternative to conventional treatments for atopic dermatitis, paving the way for more effective and safer topical therapies.
Reference
Conte, Raffaele, et al. “Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Containing Resveratrol-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles as an Adjuvant in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment.” Journal of Functional Biomaterials, vol. 14, no. 82, Jan. 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14020082.
