Editor: Nina
This study explores the therapeutic potential of newly fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) loaded with nitazoxanide and garlic extract in effectively reducing Cryptosporidium oocyst shedding and associated tissue damage in immunocompromised mice, offering a promising alternative for treating cryptosporidiosis.
Key Preview
Research Question
The study seeks to address the effectiveness of newly fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) and their combinations with nitazoxanide (NTZ) and Allium sativum (garlic) in treating cryptosporidiosis, particularly in immunocompromised patients.
Research Design and Strategy
The research employs an experimental design involving the fabrication of ZnO-NPs and their evaluation in a murine model of cryptosporidiosis, with a focus on their therapeutic potential.
Method
The study involved the fabrication of ZnO-NPs and their loading with NTZ and garlic extract, followed by parasitological, histopathological, and oxidative stress marker assessments in infected mice.
Key Results
The highest reduction in Cryptosporidium oocyst shedding (81.5%) was observed in groups treated with NTZ, while A. sativum-loaded ZnO-NPs showed a reduction of 71.1%. Both treatments significantly improved intestinal and hepatic histopathological conditions.
Significance of the Research
This study provides promising insights into the use of ZnO-NPs as an effective therapy for cryptosporidiosis, especially in conjunction with other treatments, marking a potentially economical and environmentally friendly advancement in antiparasitic therapies.
Introduction
Cryptosporidiosis, primarily caused by the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium, poses a significant health threat globally, particularly for immunocompromised individuals. Traditional treatments have shown limited efficacy, prompting the exploration of alternative therapies. Recent developments in nanotechnology have led researchers to investigate nanoparticles as effective drug carriers. The current study focuses on the fabrication of ZnO-NPs and their potential role in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of NTZ and garlic, addressing the urgent need for effective treatments against cryptosporidiosis.
Research Team and Objective
The research team comprises Doaa A. Hamdy, Mousa A. M. Ismail, Hala M. El-Askary, Heba Abdel-Tawab, Marwa M. Ahmed, Fatma M. Fouad, and Fatma Mohamed from Beni-Suef University and Cairo University, Egypt. The study, titled “Newly Fabricated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded Materials for Therapeutic Nano Delivery in Experimental Cryptosporidiosis,” is published in Scientific Reports. The primary objective is to investigate the efficacy of ZnO-NPs as a novel therapeutic strategy against cryptosporidiosis and evaluate their effects in combination with established medications and natural extracts.
Experimental Process
1. Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs)
Key Steps:
- ZnO-NPs were synthesized using a co-precipitation method, combining aqueous solutions of zinc sulfate and sodium hydroxide. The mixture was stirred continuously at 1000 rpm for 4 hours at 60°C.
- The resulting solution, initially transparent, turned milky white, indicating nanoparticle formation.
- The precipitate was collected through centrifugation at 4500 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant containing unreacted materials was discarded, and the precipitate was washed several times with deionized water and methanol to purify the nanoparticles.
- The purified ZnO-NPs were then subjected to calcination at 350°C for 3 hours, which helped in removing any remaining impurities and stabilizing the nanoparticle structure.
Results and Key Data: - Characterization techniques, including X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), confirmed the formation of ZnO-NPs with an average size of 50-65 nm.
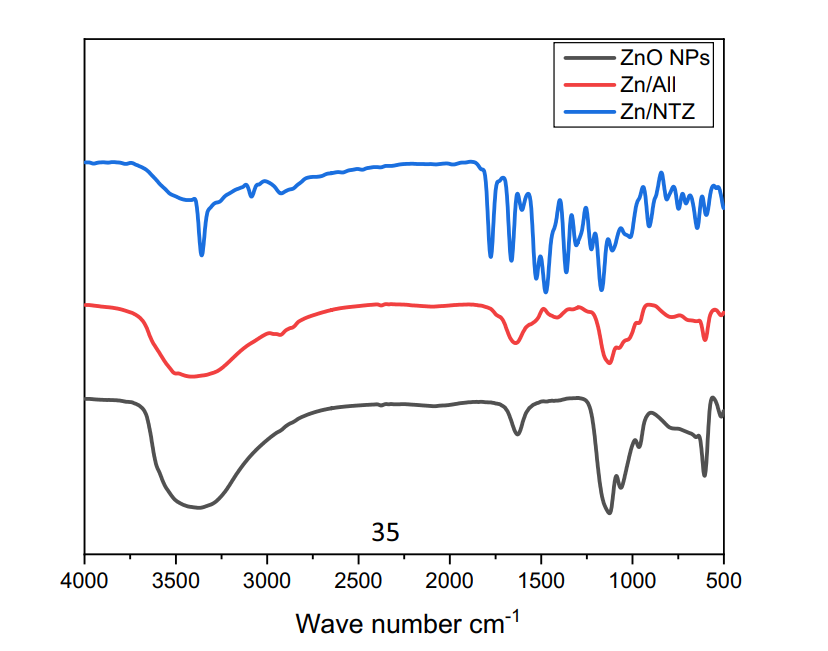
Figure 1. FTIR of ZnO-NPs, (Zn/All) and (Zn/NTZ). Te functional groups present in samples were evaluated by FTIR analysis. Te FTIR spectra were recorded within the range of 400–4000 c m−1 .
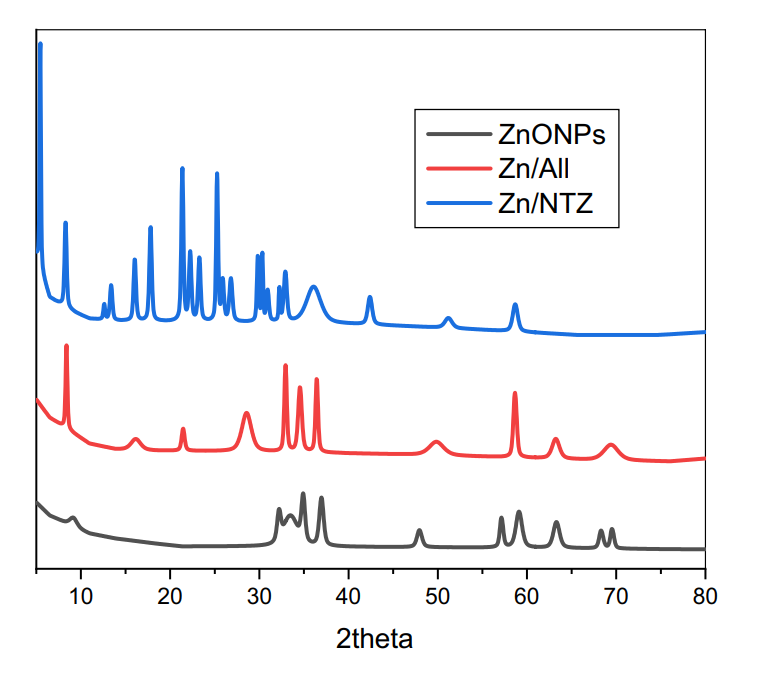
Figure 2. XRD Pattern of ZnO-NPs, (Zn/ All) and (Zn/NTZ) from 10 to 80 theta to show the crystallinity of samples.
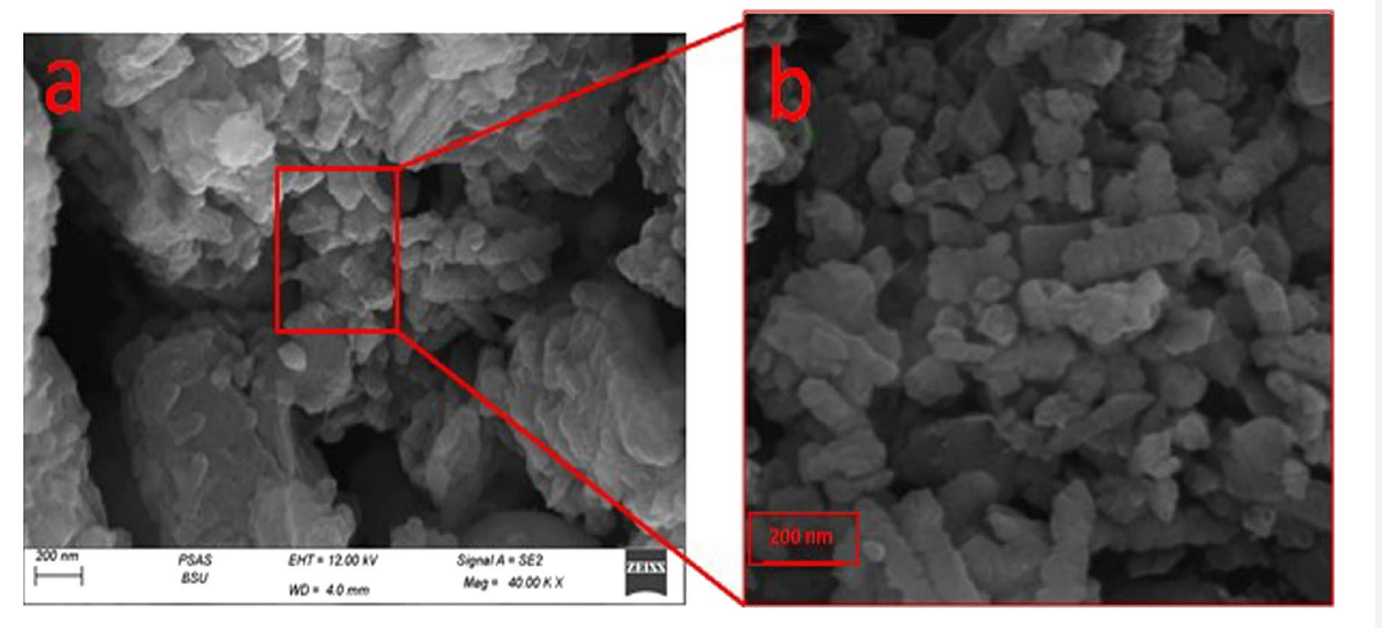
Figure 3. SEM of ZnO-NPs illustrating the surface morphology of sample.
Significance of the Result:
- The successful synthesis of ZnO-NPs demonstrates the potential for scalable production methods that are cost-effective and environmentally friendly. The controlled size and morphology of the nanoparticles are crucial for enhancing their biological activity and interaction with the target parasite.
Key Innovations: - The co-precipitation method utilized in this study is simpler and less hazardous compared to other nanoparticle synthesis techniques, such as chemical vapor deposition or laser ablation, which often require expensive equipment and toxic reagents. This innovation highlights the feasibility of adopting ZnO-NPs in a broader range of biomedical applications.
2. Loading of Therapeutics onto ZnO-NPs
Key Steps:
- Both nitazoxanide (NTZ) and garlic (A. sativum) extracts were prepared in aqueous solutions. The garlic extract was obtained by grinding fresh garlic cloves and mixing them with distilled water, followed by filtration to obtain a concentrated solution.
- ZnO-NPs were added to the NTZ solution and garlic extract separately. The mixtures were subjected to sonication for improved mixing and interaction, followed by overnight stirring at room temperature. This facilitated the adsorption of the NTZ and garlic onto the ZnO-NPs.
- After loading, the formulations were filtered to remove unbound therapeutic agents and subsequently dried to yield NTZ-loaded ZnO-NPs and A. sativum-loaded ZnO-NPs.
Results and Key Data: - Characterization via FTIR revealed the presence of functional groups from NTZ and garlic, indicating successful loading onto the ZnO-NPs. SEM images demonstrated changes in morphology, with the loaded nanoparticles exhibiting wrapped layers, which enhance the surface area for better interaction with the target cells.
Significance of the Result: - The loading of therapeutics onto ZnO-NPs significantly enhances their solubility and bioavailability, thereby improving therapeutic efficacy. This dual-loading approach offers a synergistic effect, combining the antiparasitic action of NTZ with the antioxidant properties of garlic.
Key Innovations: - This method represents an advancement in nano-delivery systems as it leverages the natural therapeutic properties of garlic alongside synthetic drugs, which is not commonly employed in traditional nanoparticle formulations. This combination allows for a more holistic treatment approach that addresses multiple mechanisms involved in cryptosporidiosis pathology.
3. In Vivo Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy
Key Steps:
- Thirty immunosuppressed Swiss albino mice were utilized in this study. They underwent immunosuppression via oral administration of dexamethasone for 15 days prior to infection to create a model that closely resembles the immune-compromised state often seen in patients affected by cryptosporidiosis.
- Mice were infected with Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts, and later divided into six groups, including control and treatment groups. Treatment commenced 7 days post-infection, with each group receiving a different formulation (ZnO-NPs, NTZ, NTZ-loaded ZnO-NPs, and A. sativum-loaded ZnO-NPs) for a duration of 5 days.
Results and Key Data: - On day 21 post-infection, oocyst shedding was quantitatively assessed. The NTZ-treated group exhibited an 81.5% reduction in oocyst shedding, while the A. sativum-loaded ZnO-NPs group showed a significant 71.1% reduction. This was statistically significant compared to the positive control group (infected, untreated).
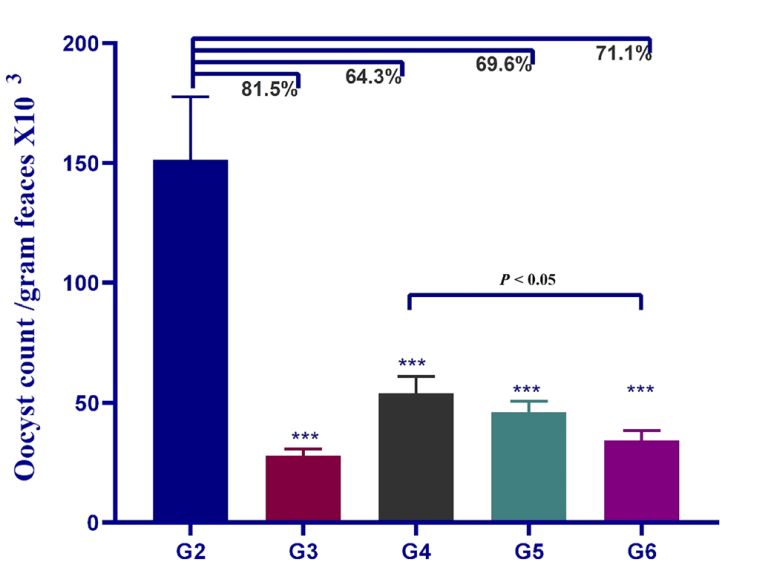
Figure 4. Mean oocyst count among the diferent groups. G2.C. parvum infected non-treated group. G3. C. parvum infected mice treated with NTZ. NPs treatment groups: G4. C. parvum infected mice treated with ZnONPs. G5. C. parvum infected mice treated with NTZ loaded on ZnO-NPs. G6. C. parvum infected mice treated with A. sativum loaded on ZnO-NPs. Triple asterisks indicated a statistical signifcance at P < 0.001 (n = 5).
Significance of the Result:
- The reduction in oocyst shedding indicates that the ZnO-NP formulations are effective in controlling the infection, which is particularly important for immunocompromised individuals who are at higher risk for severe disease.
Key Innovations: - The study’s approach of utilizing ZnO-NPs as delivery vehicles for both a synthetic drug and a natural extract represents a novel strategy that enhances therapeutic outcomes. This dual-action system is advantageous over traditional treatments, which typically involve a single therapeutic agent that may not address the multifaceted nature of cryptosporidiosis.
4. Histopathological and Oxidative Stress Assessment
Key Steps:
- Following treatment, tissue samples from the small intestine, liver, and lungs of sacrificed mice were collected. These samples were fixed in 10% formalin, sectioned, and stained using hematoxylin and eosin for histopathological analysis.
- Tissue homogenates were prepared to measure levels of oxidative stress markers, including glutathione (GSH), nitric oxide (NO), and malondialdehyde (MDA). The assays followed established biochemical protocols to quantify these markers.
Results and Key Data: - Histopathological examinations revealed that treated groups had significantly improved tissue architecture, with normal intestinal villi and reduced inflammation. The oxidative stress assessment showed that treated mice had elevated GSH levels and reduced NO and MDA levels compared to the control groups.
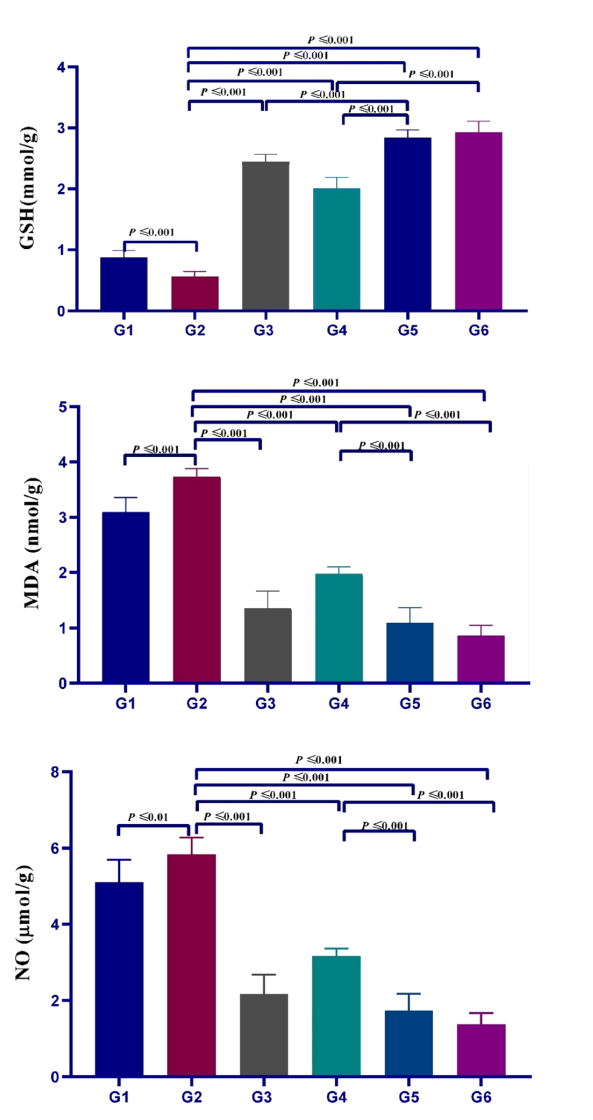
Figure 5. Efect of variable treatment regimens used in the study on GSH, MDA, and NO levels in ileum of infected mice with Cryptosporidium. Values were enumerated as mean ± SEM (n = 5).
Significance of the Result:
- The observed improvements in histopathology and oxidative stress markers underscore the therapeutic potential of ZnO-NP formulations in mitigating tissue damage and oxidative stress caused by C. parvum infection. This is crucial for improving the quality of life and recovery in immunocompromised individuals.
Key Innovations: - By integrating oxidative stress reduction into the treatment strategy, this study highlights the multifaceted benefits of ZnO-NPs as both drug carriers and potential antioxidants. This innovation contrasts with conventional therapies that often do not consider the oxidative damage accompanying parasitic infections, thus providing a more comprehensive treatment approach.
Conclusion
The study concludes that ZnO-NPs represent a promising advancement in the treatment of cryptosporidiosis. The findings highlight that the combination of ZnO-NPs with NTZ and A. sativum not only reduces parasitic oocyst shedding but also ameliorates tissue damage in infected mice. However, the study acknowledges limitations, including the lack of in vitro evaluations and the need for further research to establish optimal dosing regimens and explore additional nanoparticle combinations. Future investigations should aim to elucidate the mechanisms behind the observed therapeutic effects and the potential for clinical applications in humans.
This research underscores the critical need for innovative approaches in combatting parasitic infections, particularly for vulnerable populations, and paves the way for future advancements in nanomedicine.
Reference
Hamdy, Doaa A., et al. “Newly fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded materials for therapeutic nano delivery in experimental cryptosporidiosis.” Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 19650.
