This study presents a novel oral insulin formulation utilizing insulin-conjugated silver sulfide quantum dots coated with a chitosan/glucose polymer, demonstrating enhanced absorption and efficacy in reducing blood glucose levels without the risk of hypoglycemic episodes in both diabetic rodent models and non-diabetic baboons.
Key Preview
Research Question
The study investigates the potential of a novel oral nanotherapeutic formulation of insulin that aims to reduce the risk of hypoglycemic episodes, a common and dangerous side effect of traditional insulin therapy.
Research Design and Strategy
The research employs a combination of nanotechnology and polymer chemistry to create an insulin delivery system, specifically using insulin-conjugated silver sulfide quantum dots coated with a chitosan/glucose polymer. The study focuses on evaluating the formulation’s absorption, efficacy, and safety through a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Method
The researchers synthesized insulin-conjugated quantum dots and tested their performance in human duodenal explants and several animal models, including diabetic rodents and non-diabetic baboons, to assess blood glucose levels and potential side effects.
Key Results
The formulation demonstrated a significant reduction in blood glucose levels without inducing hypoglycemia or weight gain in diabetic rodents. In addition, non-diabetic baboons showed a dose-dependent reduction in blood glucose after administration of the oral formulation, with no observed toxicity across all tested species.
Significance of the Research
This research represents a significant advancement in diabetes management, offering a potential oral alternative to injectable insulin with fewer side effects, particularly hypoglycemic episodes, which can be life-threatening.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus poses a major global health challenge, affecting around 425 million people worldwide, with approximately 75 million relying on insulin therapy. Traditional insulin delivery methods, predominantly injections, are effective but carry risks of hypoglycemia, which can severely impact patients’ quality of life and lead to serious health complications. Recent innovations in drug delivery systems, particularly through nanotechnology, have opened avenues for safer insulin delivery methods. This study introduces a novel oral formulation aiming to minimize hypoglycemic events while effectively managing blood glucose levels.
Research Team and Objective
The research team, led by Nicholas J. Hunt and including experts from various institutions, conducted this study from January 2023 to November 2023. The paper titled “Oral Nanotherapeutic Formulation of Insulin with Reduced Episodes of Hypoglycemia” was published in Nature Nanotechnology. The primary objective was to create a safe and effective oral insulin delivery system that could mitigate the risks associated with injectable insulin therapy.
Experimental Process
The experimental process involved several key procedures to develop and evaluate the novel oral insulin nanotherapeutic formulation. Below are the outlined key steps for each experiment, along with corresponding results, significance, and innovations.
1. Synthesis of Insulin-Conjugated Quantum Dots (QD-INS)
Key Steps:
- Preparation: Silver sulfide quantum dots (Ag2S QDs) were synthesized by mixing silver diethyldithiocarbamate and 1-dodecanethiol in a vacuum environment, heated to 200 °C.
- Conjugation: The synthesized QDs were then conjugated with insulin using EDC/NHS coupling at pH 9 to facilitate chemical bonding between the QDs and insulin.
Results and Key Data:
- The conjugation process resulted in a stable QD-INS solution with a loading capacity of approximately 80%, indicating an effective attachment of insulin to the QDs.
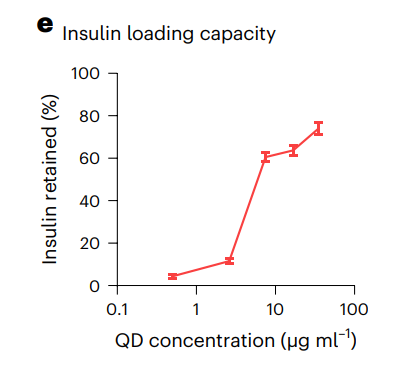
Figure 1. e, Percentage of insulin retained following attachment was dependent on the QD concentration; increasing the QDs (more binding sites) promoted greater insulin retainment.
Significance of the Result:
- This successful synthesis of QD-INS demonstrates potential for enhanced oral bioavailability, as it maintains insulin’s structural integrity during the formulation process.
Key Innovations:
- The use of Ag2S QDs offers a robust foundation for drug delivery, which enhances absorption compared to traditional insulin delivery methods that often suffer from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract.
2. Coating with Chitosan/Glucose Polymer (CS/GS)
Key Steps:
- Polymer Synthesis: A random copolymer of chitosan and glucose was synthesized via hydrolysis and condensation polymerization.
- Coating Application: The QD-INS was then coated with CS/GS through electrostatic interactions at neutral pH, effectively forming QD-INS-CS/GS nanoparticles.
Results and Key Data:
- The final product demonstrated a hydrodynamic diameter of approximately 20 nm, indicating successful formation of nanoparticles.
- The coating significantly improved the stability of the insulin formulation in acidic environments, with the QD-INS-CS/GS remaining insoluble at pH levels below 6.
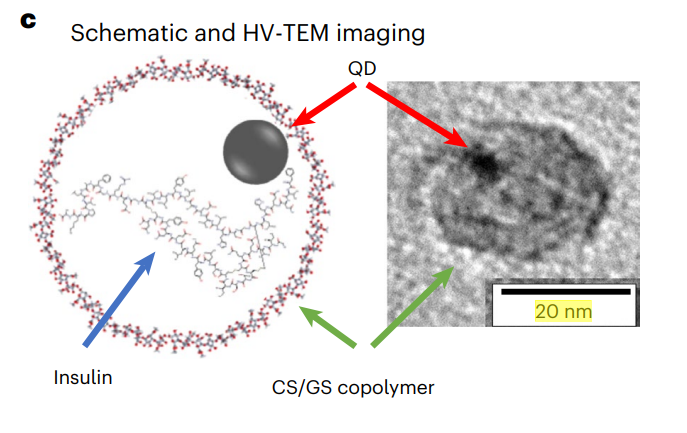
Figure 2. c, HV-TEM imaging shows the spherical 20 nm nanoparticles containing Ag2S QDs.
Significance of the Result:
- The CS/GS coating protects the insulin payload from harsh gastric conditions, ensuring that insulin remains intact until it reaches the desired site of absorption in the intestine.
Key Innovations:
- This approach combines the benefits of pH-responsive materials with nanotechnology, improving targeted delivery and absorption of insulin compared to traditional polymeric formulations, which may lack such specificity.
3. In Vitro Testing with Human Duodenal Explants
Key Steps:
- Experimental Setup: Human duodenal explants were incubated with QD-INS-CS/GS to assess absorption efficacy.
- Data Collection: The amount of insulin absorbed by the explants was measured over a 2-hour period.
Results and Key Data:
- The QD-INS-CS/GS formulation achieved a 40-fold increase in insulin uptake compared to free insulin.
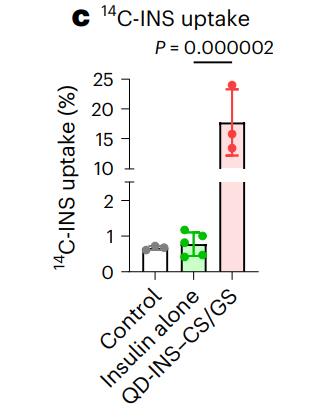
Figure 3. c, Quantification of 14C-INS uptake was evaluated in explants following a 2-h incubation at 37 °C conjugation of insulin with QD-INS–CS/GS leading to a 40-fold increase in insulin uptake compared with insulin alone.
Significance of the Result:
- This result signifies that the formulation can enhance the absorption of insulin in the intestinal environment, a critical factor for effective oral delivery.
Key Innovations:
- The enhanced uptake showcases the superior performance of QD technology over traditional delivery systems, which often result in limited absorption and efficacy.
4. In Vivo Evaluations in Diabetic Rodents
Key Steps:
- Treatment Administration: Diabetic rodents received oral doses of QD-INS-CS/GS to evaluate blood glucose response.
- Monitoring: Blood glucose levels were monitored pre- and post-administration over a specified duration.
Results and Key Data:
- The treatment resulted in a significant dose-dependent reduction in blood glucose levels without inducing hypoglycemia or weight gain in the animals.
Significance of the Result:
- The findings indicate that the formulation effectively manages blood glucose levels while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemic events, a critical concern in insulin therapy.
Key Innovations:
- This formulation demonstrates a targeted approach to insulin delivery, contrasting with traditional methods that often require careful dosing to avoid hypoglycemia.
5. Toxicity Assessments in Animal Models
Key Steps:
- Toxicity Testing: The safety profile of QD-INS-CS/GS was evaluated in multiple animal models, including C57BL/6 mice and STZ-treated diabetic rats.
- Biochemical Analysis: Blood samples were collected to assess potential biochemical or hematological changes.
Results and Key Data:
- No adverse biochemical or hematological toxicity was observed, indicating a favorable safety profile for the QD-INS-CS/GS formulation.
Significance of the Result:
- Establishing safety is crucial for any new drug delivery system, particularly for chronic conditions like diabetes that rely on long-term medication.
Key Innovations:
- The formulation’s compatibility and safety in animal models provide a significant advantage over traditional formulations that may have higher toxicity profiles due to their chemical constituents.
Conclusion
The study successfully demonstrates that the newly developed oral insulin nanotherapeutic formulation can effectively manage blood glucose levels without the common side effect of hypoglycemia. This advancement could revolutionize diabetes treatment, offering a safer alternative for insulin-dependent patients. However, the research acknowledges limitations, including the need for further clinical trials to confirm efficacy and safety in humans. Future research may focus on optimizing the formulation and evaluating its long-term effects in larger clinical populations.
In summary, this formulation holds promise for improving the lives of millions of individuals living with diabetes, making insulin therapy more accessible and safer.
