Editor: Nina
This study demonstrates that a combined nano-formulation of curcumin and resveratrol effectively reduces hyperammonemia and its associated hepatic and neurological complications in rats subjected to a protein-deficient diet, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic strategy for malnutrition-related hyperammonemia, particularly in pediatric populations.
Key Preview
Research Question
This study investigates whether a nano-formulation combining curcumin and resveratrol can effectively combat hyperammonemia induced by a protein-deficient diet (PDD) in rats.
Research Design and Strategy
The research employed a controlled experiment with male juvenile albino rats divided into various groups, including those receiving different dosages of the nano-formulation and a control group.
Method
The rats were subjected to a PDD for 75 days, followed by treatment with curcumin, resveratrol, or a combination of both in nanoemulsion form for 15 days. Various biochemical parameters were assessed post-treatment.
Key Results
The combined nano-formulation significantly reduced ammonia levels in the liver and brain, normalized liver enzymes (ALT and AST), and improved neurotransmitter levels compared to the control group.
Significance of the Research
This research highlights the potential of curcumin-resveratrol nano-formulations as an innovative therapeutic strategy to address hyperammonemia, particularly important for pediatric populations at risk due to malnutrition.
Introduction
The understanding of hyperammonemia, characterized by elevated ammonia levels in the bloodstream, has evolved significantly over the years. It is now recognized as a critical factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and various neurological disorders. Traditional treatments have often been limited by the poor bioavailability of therapeutic agents. This study introduces a novel approach by utilizing a nano-formulation of curcumin and resveratrol, both known for their hepatoprotective and neuroprotective properties.
The primary research question addresses how effectively this combination can mitigate the adverse effects of hyperammonemia induced by a protein-deficient diet (PDD) in rats. Given the rising incidence of malnutrition-related hyperammonemia, particularly in pediatric populations, this research is crucial for developing effective interventions.
Research Team and Objective
The research was conducted by a team comprising Maha Nasr, Omar A. H. Ahmed-Farid, and Rania F. Ahmed, affiliated with institutions in Cairo, Egypt. The study, titled “Curcumin-resveratrol nano-formulation counteracting hyperammonemia in rats,” was published in the journal Metabolic Brain Disease. The objective is to explore the therapeutic effects of a combined curcumin-resveratrol nanoemulsion in ameliorating PDD-induced hyperammonemia and its related complications.
Experimental Process
1. Preparation of Nanoemulsions
Key Steps:
- Curcumin and resveratrol were individually dissolved in Labrafac Lipophile oil (10% w/v) and Cremophor RH surfactant (10% w/v).
- The solutions were gradually introduced into a magnetically-stirred aqueous phase at room temperature to create spontaneous emulsifications.
- Characterization of the nanoemulsions was performed using a Zetasizer device to assess particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential.
Results and Key Data:
- The prepared curcumin nanoemulsion exhibited a particle size of 136 nm, while the resveratrol nanoemulsion showed a particle size of 128 nm. The combined nanoemulsion displayed a particle size of 135 nm.
- Zeta potential values were recorded at approximately -17.89 mV for curcumin, -15.92 mV for resveratrol, and -18.93 mV for the combined formulation.
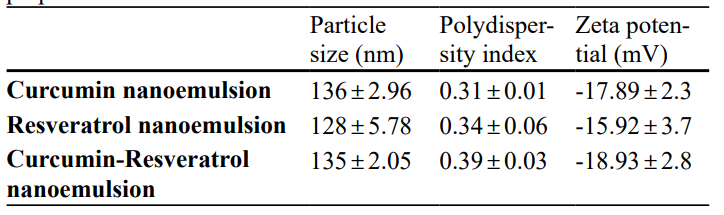
Table 1. Particle size, polydispersity index and zeta potential of the prepared nanoemulsions.
Significance of the Result:
- The small particle size and negative zeta potential indicate enhanced stability and prolonged circulation time in the bloodstream, which is crucial for effective delivery of the active compounds.
Key Innovations:
- The use of spontaneous emulsification provides a simpler and more efficient method to create nanoemulsions compared to traditional high-energy methods. This approach minimizes the risk of degradation of sensitive compounds like curcumin and resveratrol, enhancing their bioavailability.
2. Animal Model
Key Steps:
- Male Wistar albino rats were acclimatized for one week and then divided into eight groups, with one control group fed a normal diet and seven experimental groups subjected to a PDD consisting of shelled corn grains for 75 days.
- Drug administration of varying doses of the nanoemulsions (curcumin, resveratrol, and their combination) commenced on day 61 and continued for 15 days.
Results and Key Data:
- The control group maintained normal physiological parameters, while the PDD group showed significant weight loss and signs of malnutrition.
Significance of the Result:
- This step established a reliable model of hyperammonemia, enabling the assessment of the therapeutic effects of the nano-formulation.
Key Innovations:
- The study utilized a well-characterized animal model that reflects hyperammonemia conditions often seen in malnourished pediatric populations, enhancing the translational potential of the findings.
3. Treatment Administration
Key Steps:
- After the 75-day PDD, treatment groups received oral doses of the nanoemulsions (2.5 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg for individual compounds, and 2.5 + 2.5 mg/kg and 5 + 5 mg/kg for the combination) for 15 days.
- The control group continued receiving distilled water.
Results and Key Data:
- Rats receiving the combined nanoemulsion at the higher dose showed a significant reduction in serum ammonia levels by 63% compared to the PDD control group.
Significance of the Result:
- This reduction in ammonia levels indicates that the combined nanoemulsion effectively mitigates the hyperammonemia induced by PDD, suggesting potential therapeutic applications.
Key Innovations:
- The use of a combined formulation allows for synergistic effects of curcumin and resveratrol, which may enhance therapeutic outcomes compared to administering each compound separately.
4. Biochemical Analysis
Key Steps:
- Post-treatment, blood samples were collected for serum ALT and AST measurements, while liver and brain tissues were analyzed for ammonia, NOx, 8-OHdG, ATP, ADP, AMP, and neurotransmitter levels (5-HT, NE, DA, and glutamate).
- Specific assays for each biochemical parameter were performed using spectrophotometry and HPLC techniques.
Results and Key Data:
- The combined nanoemulsion resulted in normalization of serum ALT and AST levels, reduction of hepatic ammonia levels by 77.19%, and restoration of neurotransmitter levels (e.g., serotonin increased by 31.86%).
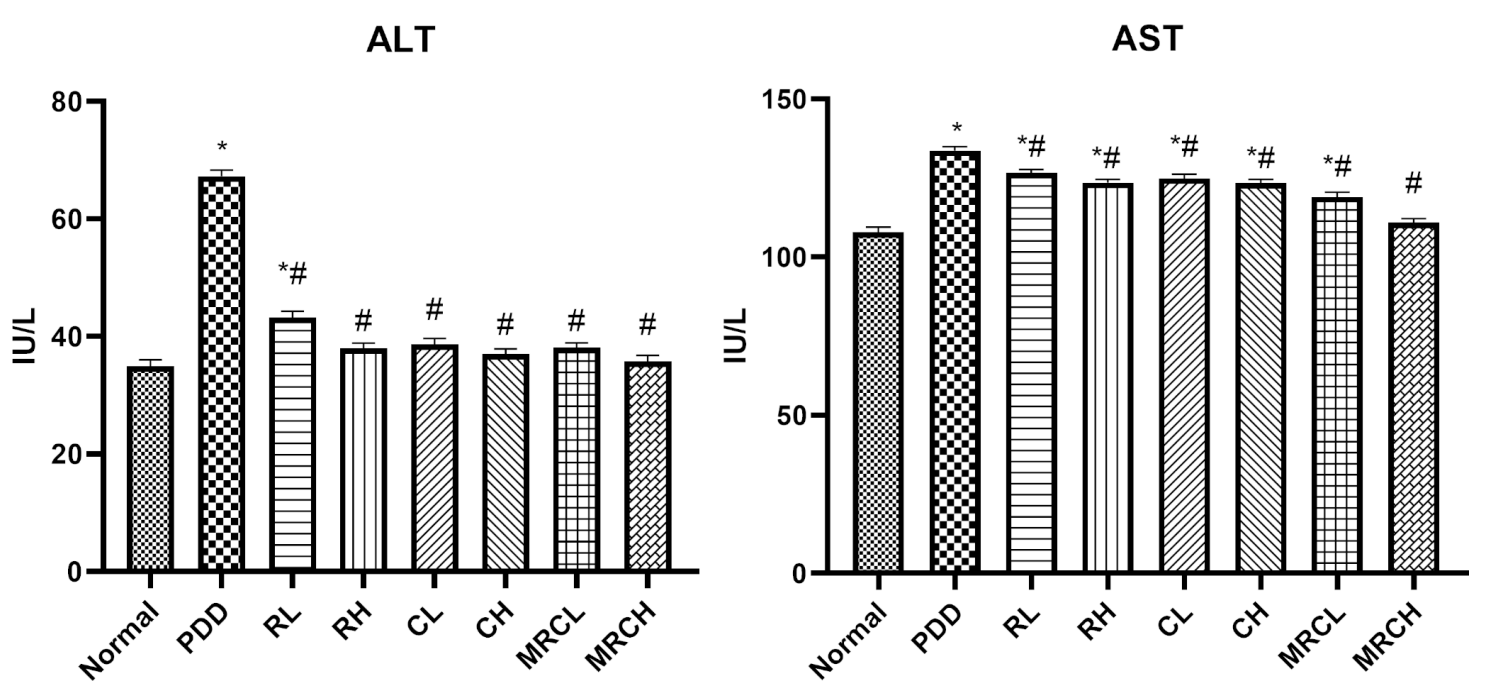
Figure 1. Impact of different treatments on serum hepatic enzymes ALT and AST. * Signiffcance vs. normal, # signiffcance vs. PDD control.
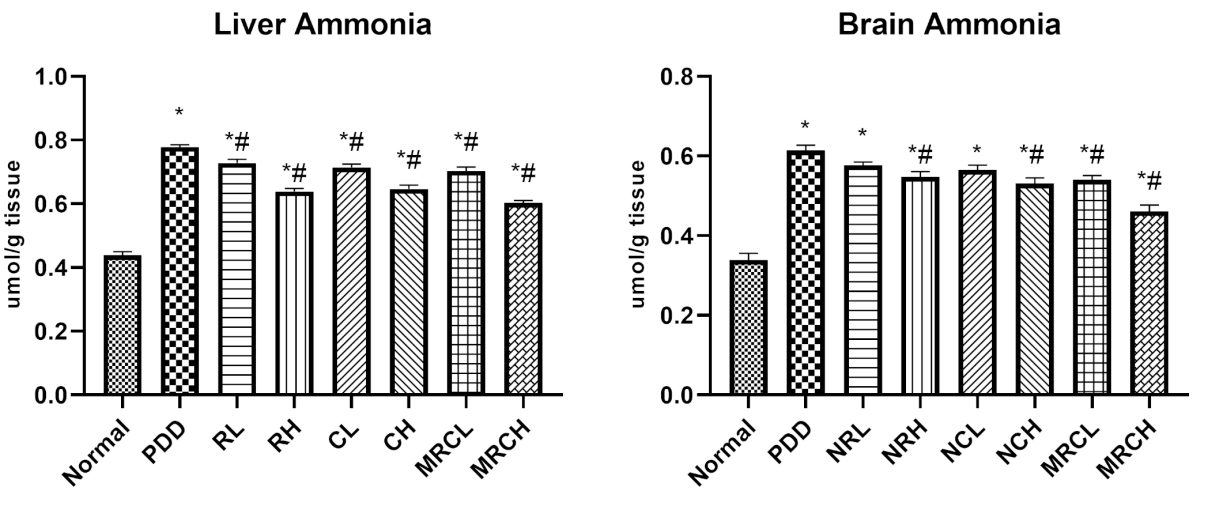
Figure 2. Impact of different treatments on hepatic and brain ammonia levels. * Signiffcance vs. normal, # signiffcance vs. PDD control.
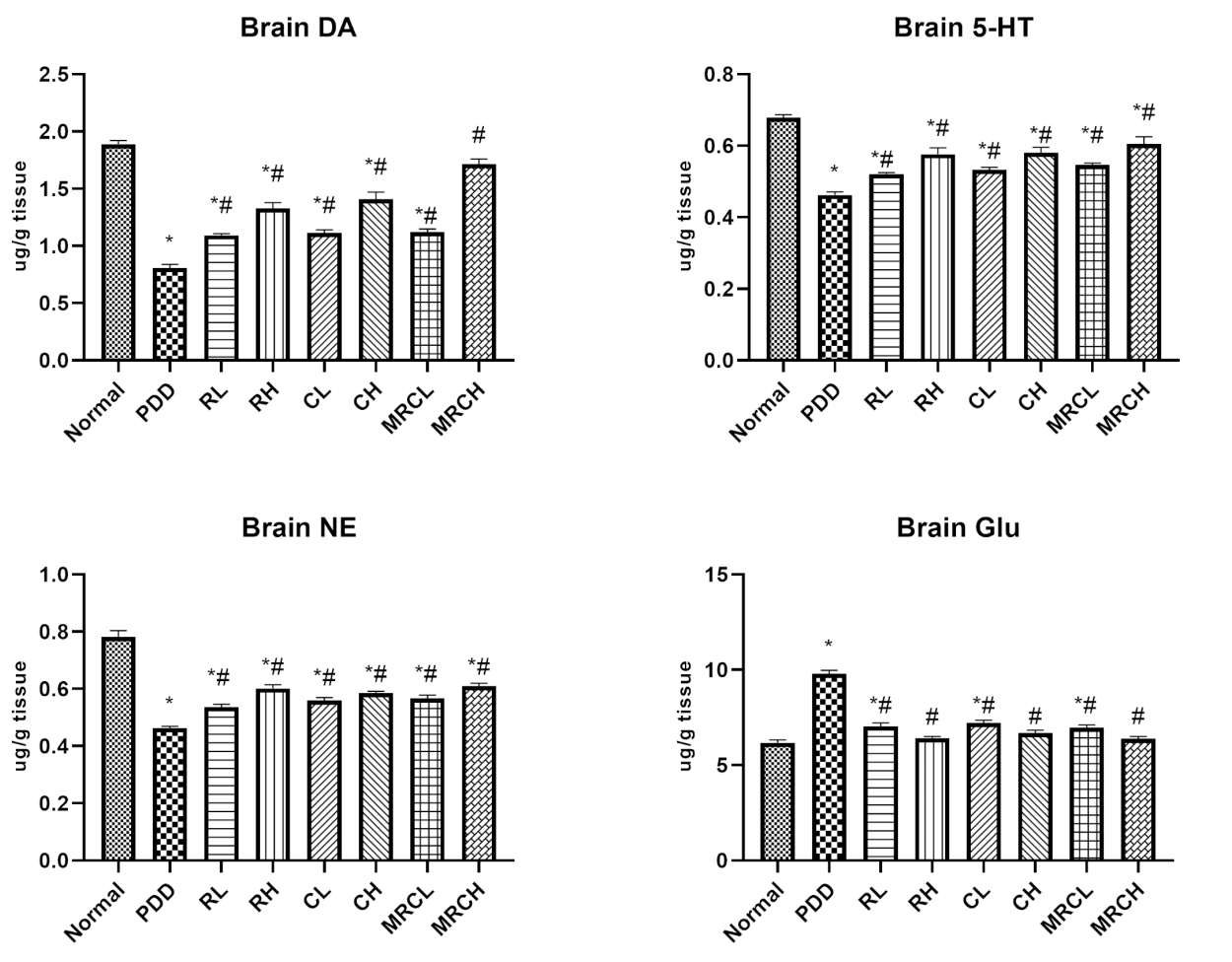
Figure 3. Impact of different treatments on brain monoaminergic neurotransmitters and glutamate levels. * Significance vs. normal, # significance vs. PDD control
Significance of the Result:
- These biochemical markers indicate improved liver function and neuroprotection, reinforcing the effectiveness of the treatment in addressing hyperammonemia and its neurological implications.
Key Innovations:
- The comprehensive biochemical analysis provided insights into multiple pathways affected by hyperammonemia, showcasing the multifunctional benefits of the nano-formulation.
5. Statistical Analysis
Key Steps:
- One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was employed to analyze the data, with a significance level set at p < 0.05.
Results and Key Data:
- Statistical analyses confirmed that all treatment groups significantly differed from the PDD control group, validating the efficacy of the nano-formulation.
Significance of the Result:
- Robust statistical validation enhances the reliability of the findings, providing a strong basis for future research and potential clinical applications.
Key Innovations:
- The application of rigorous statistical methods ensures that the results are not only significant but also reproducible, a crucial aspect in preclinical research.
Conclusion
The study concluded that the combined nano-formulation of curcumin and resveratrol effectively mitigated the hepatic and cerebral adverse effects associated with PDD-induced hyperammonemia in rats. This finding underscores the potential of utilizing such formulations in clinical settings, particularly for the pediatric population suffering from malnutrition-related hyperammonemia.
However, the study acknowledged limitations, including the lack of histological examinations, which could provide deeper insights into the therapeutic effects. Future research should focus on quantifying neurodegeneration and exploring the effectiveness of this treatment strategy in clinical scenarios involving pediatric patients.
Overall, this research contributes valuable knowledge to the field of nutritional interventions and pharmacological strategies for managing hyperammonemia, paving the way for future studies aimed at addressing this critical health challenge.
Reference:
Nasr, Maha, Omar AH Ahmed-Farid, and Rania F. Ahmed. “Curcumin-resveratrol nano-formulation counteracting hyperammonemia in rats.” Metabolic Brain Disease 38.4 (2023): 1365-1377.
