Editor: Nina
This study presents a curcumin-zinc framework encapsulated microneedle patch (ZnMOF-MN) as an innovative and effective transdermal delivery system that significantly promotes hair growth by addressing oxidative stress and zinc deficiency in hair loss conditions
Key Preview
Research Question
Can a curcumin-zinc framework encapsulated microneedle patch effectively promote hair growth while addressing hair loss conditions, particularly those related to zinc deficiency and oxidative stress?
Research Design and Strategy
The study utilized a combination of in vitro and in vivo experiments to assess the effectiveness of a novel curcumin-zinc framework (ZnMOF) encapsulated in a gamma-polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA) microneedle patch (ZnMOF-MN) for promoting hair growth.
Method
The research involved synthesizing ZnMOF, characterizing its properties, and evaluating its effects on mouse dermal papilla cells (DPCs). It also tested the ZnMOF-MN patch in two animal models: an androgenic alopecia (AGA) model and a wound healing model.
Key Results
The ZnMOF-MN patch demonstrated significant improvements in hair regrowth, enhanced cell proliferation, and accelerated wound healing. It increased viability of DPCs against oxidative stress and reversed adverse effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Significance of the Research
This research provides a promising approach to treating hair loss through a multifunctional, biosafe transdermal drug delivery system that addresses multiple underlying issues, including oxidative stress and zinc deficiency.
Introduction
Hair loss presents a significant aesthetic concern, with up to 85% of males and 40% of females experiencing some form of hair condition. Traditional treatments often target specific aspects of hair loss but overlook the complex interplay of factors such as oxidative stress and nutrient deficiencies. This research builds on previous studies indicating the detrimental effects of zinc deficiency on hair growth and the antioxidant properties of curcumin. The study introduces a novel microneedle patch that encapsulates curcumin and zinc ions, designed to deliver these compounds directly to the dermal layer, maximizing their therapeutic effects. The central research question focuses on whether this innovative delivery system can effectively promote hair growth under conditions characterized by oxidative stress and hormonal imbalances.
Research Team and Objective
The study was conducted by Yating Yang, Pei Wang, Yan Gong, Ziyou Yu, Yuci Gan, Peizhe Li, Wei Liu, and Xiansong Wang, affiliated with the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. Published in the journal Theranostics, the objective of the research was to develop and evaluate the efficacy of a curcumin-zinc framework encapsulated microneedle patch in promoting hair growth, particularly in models of androgenic alopecia and wound healing.
Experimental Process
1. Synthesis of ZnMOF
Key Steps:
- Preparation: A solution of zinc sulfate heptahydrate (100 mg) was dissolved in 10 mL deionized water. Separately, curcumin (120 mg) was dissolved in 10 mL of alkaline water (pH 12) adjusted with 10 mol/L KOH.
- Mixing: The curcumin solution was then combined with the zinc solution and stirred to ensure thorough mixing.
- Heating: The mixture was heated at 50 °C for 24 hours in a muffle furnace to facilitate the formation of ZnMOF crystals.
- Separation and Washing: The resultant solid was isolated via centrifugation (12,000 rpm for 15 minutes) and washed with 95% ethanol and deionized water to remove impurities.
Results and Key Data:
- The synthesized ZnMOF appeared as cone-shaped nanoparticles, with a size distribution of 424.9 ± 59.01 nm, confirmed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS).
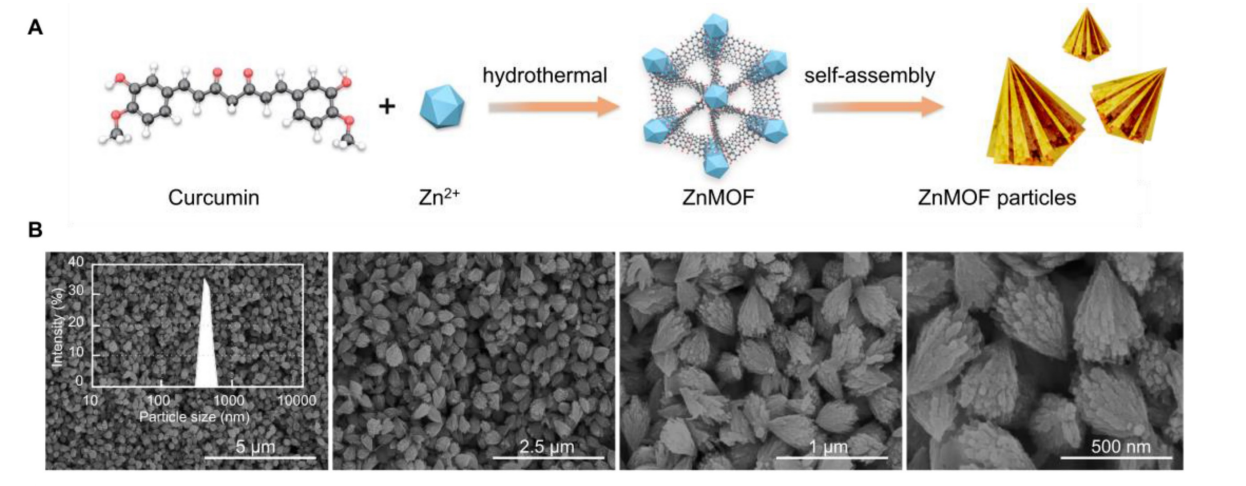
Figure 1. A. Schematic illustration of the synthesis of ZnMOF microsphere. B. FE-SEM image and size distribution of ZnMOF
Significance of the Result:
- The successful synthesis of ZnMOF with controlled size and morphology is crucial for enhancing the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of the encapsulated curcumin and zinc ions.
Key Innovations:
- The incorporation of curcumin within a metal-organic framework represents a novel approach to increase the stability and controlled release of bioactive compounds, which is often a limitation in traditional delivery systems.
2. Fabrication of ZnMOF-MN Patch
Key Steps:
- Preparation of Hydrogel: The synthesized ZnMOF was combined with gamma-polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA) to create a hydrogel.
- Microneedle Fabrication: The hydrogel was filled into commercial PDMS molds designed to create microneedles, which were then dried at 40 °C overnight to form solid microneedles.
Results and Key Data:
- The ZnMOF-MN patches exhibited pyramid-shaped tips with an average height of 466.23 ± 11.72 μm. The patches showed 90% dissolution within 25 minutes upon exposure to moisture, indicating rapid hydrogel formation upon application.
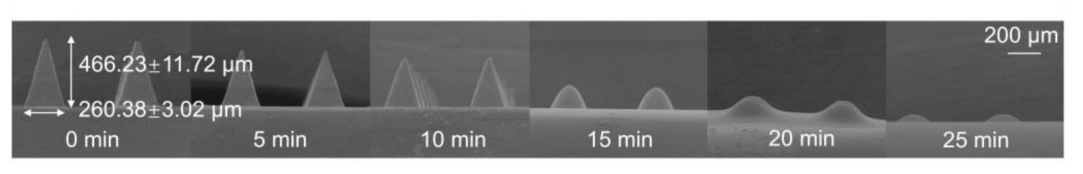
Figure 2. SEM images of ZnMOF-MN tips after moisture absorption at different time points (75% humidity, 25 °C). The labels revealed the detailed dimensions of the MN tips: a base diameter of 260.38 ± 3.02 μm and a height of 466.23 ± 11.72 μm.
Significance of the Result:
- The ability to create temporary perforations in the skin with minimal discomfort allows for efficient transdermal delivery of therapeutic agents directly to the targeted dermal layer.
Key Innovations:
- The use of a soluble polymer (γ-PGA) for microneedle fabrication, combined with the ZnMOF, enhances biodegradability and biocompatibility, representing a significant improvement over traditional non-biodegradable microneedle systems.
3. In Vitro Studies on DPCs
Key Steps:
- Cell Culture: Mouse dermal papilla cells (DPCs) were cultured and treated with varying concentrations of ZnMOF solution and ZnMOF-MN extracts.
- Oxidative Stress Simulation: Cells were exposed to H2O2 to induce oxidative stress, followed by viability assessment using the CCK-8 assay.
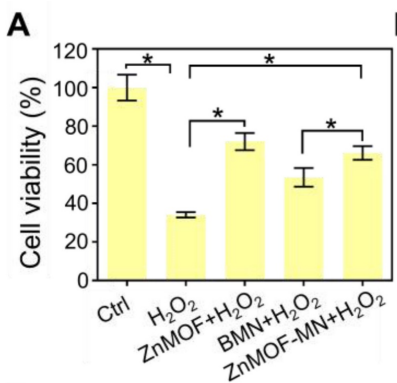
Figure 3. Cell viability of DPCs treated with 5 μg mL−1 ZnMOF solution, BMN extract, or ZnMOF-MN extract (~6.46 μg mL−1 ZnMOF) for 24 h and then incubated with 3 mM H2O2 for 30 min.
Results and Key Data:
- ZnMOF and ZnMOF-MN extracts significantly improved DPC viability against H2O2-induced oxidative stress, demonstrating cell viability rates of over 80% compared to less than 30% in untreated controls.
Significance of the Result:
- The ability of ZnMOF to counteract oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in DPCs directly correlates with its potential to promote hair growth under stress conditions.
Key Innovations:
- The dual action of curcumin as an antioxidant and zinc as a vital nutrient, combined in a single delivery system, enhances the therapeutic effects compared to traditional treatments that focus on either aspect separately.
4. In Vivo Wound Healing Model
Key Steps:
- Model Establishment: Full-thickness wounds were created on the backs of male C57BL/6 mice. The ZnMOF-MN patches were applied once on day 0 post-wound creation.
- Healing Monitoring: Wound closure was monitored through photographic documentation and measurement of wound area over 17 days.
Results and Key Data:
- The ZnMOF-MN group exhibited a significantly faster wound closure rate, with an average wound area reduction of 76.45% by day 11, compared to only 27.84% in the control group.
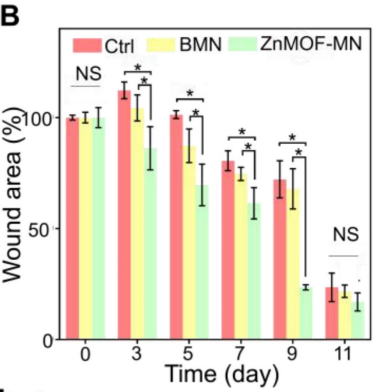
Figure 4. B. Quantification of the wound area rate in each group on day 0, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11.
Significance of the Result:
- Accelerated wound healing not only highlights the regenerative properties of ZnMOF-MN but also reinforces its potential as a treatment for hair loss resulting from skin injury.
Key Innovations:
- The combination of enhanced angiogenesis and cell proliferation due to the ZnMOF-MN treatment represents a multifaceted approach to wound healing that is superior to traditional topical treatments.
5. In Vivo Androgenic Alopecia Model
Key Steps:
- Model Creation: Male mice were subcutaneously injected with dihydrotestosterone (DHT) to induce AGA. Treatments with ZnMOF-MN patches were administered on days 1, 4, 7, and 10.
- Hair Regrowth Evaluation: Hair regrowth was assessed visually and through histological analysis on day 18 post-treatment.
Results and Key Data:
- Mice treated with ZnMOF-MN exhibited 92.30 ± 2.32% hair coverage, significantly higher than the 32.84 ± 13.40% seen in untreated controls.
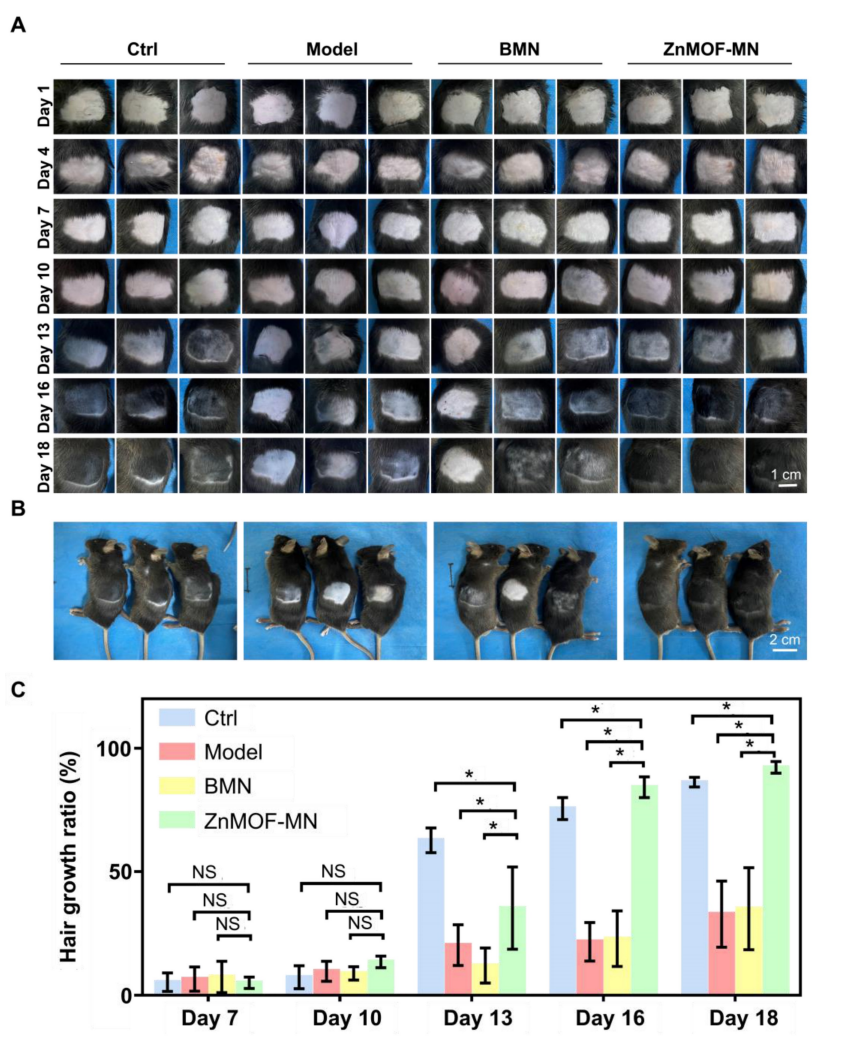
Figure 5. A. Representative images of the hair regrowth condition in different groups on day 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, and 18 after depilation. B. Gross images of hair regrowth in mice of different groups on day 18. C. Quantification of the hair growth rate in each group on days 7, 10, 13, 16, and 18. n = 5, *p < 0.05, NS refers to no significance. Ctrl for the control group.
Significance of the Result:
- This substantial improvement in hair regrowth demonstrates the effectiveness of the ZnMOF-MN patches in reversing the effects of hormonal-induced hair loss.
Key Innovations:
- The innovative use of a dual-action formulation targeting both oxidative stress and hormonal imbalances provides a comprehensive solution for hair loss, contrasting with traditional methods that typically address only one factor.
Conclusion
This research presents the ZnMOF-MN patch as an innovative and effective method for promoting hair growth. By addressing the dual challenges of oxidative stress and zinc deficiency, the patch offers a promising therapeutic avenue for treating hair loss conditions. While the findings are significant, the study acknowledges limitations, including the need for larger clinical trials to confirm efficacy in humans. Future research should focus on optimizing the formulation and assessing long-term effects and safety in diverse populations. This work underscores the potential of using advanced drug delivery systems to tackle complex health issues effectively.
Reference:
Yang, Yating, et al. “Curcumin-zinc framework encapsulated microneedle patch for promoting hair growth.” Theranostics 13.11 (2023): 3675.
