Editor: Nina
Key Preview
Research Question
– What are the effects of low solubility on the clinical application of icariin as a hepatoprotective agent?
– Can complexation with hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin (HP-γ-cyclodextrin) improve the solubility and pharmacokinetic profile of icariin?
Research Design and Strategy
– The study aimed to address the solubility limitations of icariin through complexation with HP-γ-cyclodextrin.
– A comprehensive approach was taken, combining in vitro dissolution rate assessments with in vivo pharmacokinetic studies in dogs.
– The research strategy included the use of various analytical techniques to confirm the formation and efficacy of the icariin-HP-γ-cyclodextrin complex.
Method
– The complexation of icariin with HP-γ-cyclodextrin was achieved using a solution method with the addition of a trace amount of water-soluble polymer.
– In vitro assessments included UV spectroscopy, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and thermal analyses to determine solubility and complex stability.
– In vivo pharmacokinetic studies involved oral dosing of icariin and its complex in dogs, with subsequent analysis of plasma samples to evaluate drug metabolism and distribution.
Key Results
– The complexation with HP-γ-cyclodextrin increased the water solubility of icariin by 654 times, achieving a solubility of 13.09 mg/mL.
– In vitro, the icariin complex showed a dissolution rate 80 times greater than pure icariin, with 100% release within minutes.
– In vivo, the complexation increased the Cmax of icariin by about 5 times, AUC0-120 by about 20 times, and extended the half-life from 0.68 hours to 6.38 hours.
Significance of the Research
– The study’s findings have substantial implications for the medical and pharmaceutical industries, potentially reducing the required doses of icariin for therapeutic effects.
– The improved solubility and bioavailability may lead to reduced side effects and costs associated with icariin treatment.
– This research highlights the potential of natural products in modern therapeutic development and opens new avenues for the application of icariin in hepatoprotection and anti-cancer therapies.
Introduction
Icariin, a flavonol glycoside derived from the Herba epimedii plant, has been revered for its diverse health benefits, such as the ability to expand blood vessels and enhance the immune system. Despite its therapeutic potential, the low solubility of icariin (0.02 mg/mL) has posed a significant barrier to its clinical application. This study represents a significant advancement in addressing this challenge, utilizing complexation techniques that could revolutionize the use of natural compounds in modern medicine. By overcoming the solubility issue, researchers have paved the way for further exploration of icariin’s therapeutic roles.
Research Objective

The research team, including Yili Ding, Bo Yu, Shuzhen Zhou, Charles Ding, Zhiyuan Zhang, Shufeng Xu, and Zhe Xu, aimed to enhance the pharmacological efficacy of icariin through improved solubility and absorption rates. Conducted across various institutes and published in Frontiers in Pharmacology, this study not only tackles a critical challenge in drug formulation but also underscores the importance of natural products in therapeutic development.
Experimental Process: Innovative Methodologies Leading to Promising Results
This study employed a series of innovative methodologies to address the solubility and pharmacokinetic challenges of icariin, a naturally occurring hepatoprotective agent. The key methodologies included complexation with HP-γ-cyclodextrin, in vitro dissolution testing, and in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation. These approaches led to promising results, significantly enhancing the therapeutic potential of icariin.
Key Experimental Procedures and Results
1. Complexation with HP-γ-Cyclodextrin
– Key Steps: Icariin was complexed with HP-γ-cyclodextrin using a solution method, involving the slow addition of icariin in ethanol to an HP-γ-cyclodextrin solution in water, followed by stirring at a controlled temperature and speed.
– Result: This method achieved a remarkable increase in icariin’s water solubility to 13.09 mg/mL, a 654-fold improvement over the native solubility of icariin.
– Significance: This substantial increase in solubility addresses the primary limitation of icariin, making it a more viable candidate for pharmaceutical applications.
– Innovation: The use of HP-γ-cyclodextrin and a trace amount of water-soluble polymer was a novel approach that significantly surpassed previous solubility enhancement methods.
2. In Vitro Dissolution Testing
– Key Steps: The dissolution rate of the icariin-HP-γ-cyclodextrin complex was assessed in vitro using a dissolution meter, where the complex was exposed to water while stirring, and samples were taken at various time points for HPLC analysis.
– Result: The complex demonstrated a dissolution rate 80 times greater than that of pure icariin, with complete release within the first 10 minutes.
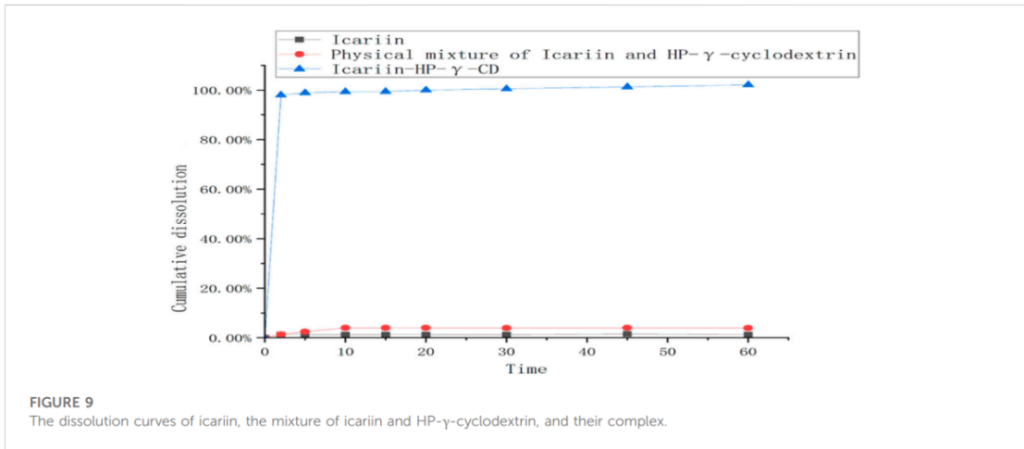
– Significance: Rapid dissolution is crucial for drugs to achieve therapeutic concentrations quickly, which can be particularly beneficial in acute conditions.
– Innovation: The accelerated dissolution rate highlights the potential of the complex to improve the bioavailability of icariin, a common challenge with poorly water-soluble drugs.
3. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
– Key Steps: Twelve healthy adult dogs were orally dosed with either icariin or the icariin-HP-γ-cyclodextrin complex, and blood samples were collected at various time points post-administration. Plasma was analyzed to determine icariin concentrations using HPLC.
– Result: The complexation with HP-γ-cyclodextrin increased the Cmax of icariin by about 5 times, AUC0-120 by about 20 times, and extended the half-life from 0.68 hours to 6.38 hours.
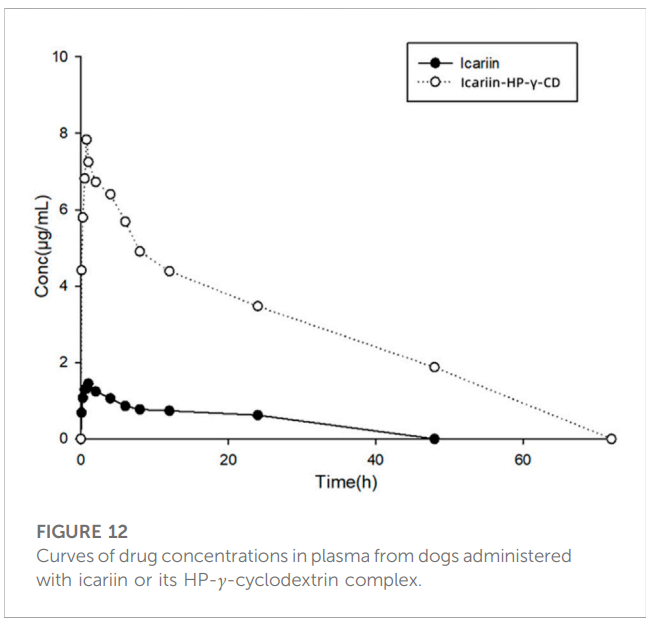
– Significance: These results indicate that the complex significantly improves the absorption and retention of icariin in the bloodstream, which could lead to more effective therapeutic outcomes.
– Innovation: The comprehensive in vivo evaluation provided a clear understanding of how the complexation affects the pharmacokinetics of icariin, offering valuable insights for its clinical development.
The innovative methodologies employed in this study have led to groundbreaking results in enhancing the solubility and pharmacokinetic profile of icariin. The key innovations include the use of HP-γ-cyclodextrin to achieve unprecedented solubility enhancement, the demonstration of rapid in vitro dissolution rates, and the significant improvement in in vivo pharmacokinetic parameters. These findings not only address the historical challenges associated with icariin but also pave the way for its potential use as a hepatoprotective and anti-cancer agent. The study’s methodologies and results underscore the importance of innovative drug delivery systems in maximizing the therapeutic potential of natural products.
Conclusion: A Path Forward for Icariin Research
The study successfully demonstrated that complexing icariin with HP-γ-cyclodextrin significantly enhances its solubility and pharmacokinetic profile, marking a critical step forward in the field of natural product pharmacology. The results indicate that this complex could serve as a viable candidate for further development as a hepatoprotector or anti-cancer agent. However, researchers acknowledge the need for additional studies to explore the long-term effects and clinical applicability of this formulation. Future research could pave the way for broader applications of icariin in medicine, potentially transforming it into a leading compound in hepatoprotection and beyond. With this breakthrough, the potential for icariin to be utilized effectively in clinical settings is more promising than ever, urging the scientific community to continue exploring natural compounds for therapeutic innovations.
Reference:
Ding, Yili, et al. “Improvement of solubility and pharmacokinetic profile of hepatoprotector icariin through complexation with HP-γ-cyclodextrin.” Frontiers in pharmacology 14 (2023): 1138686.
