
Ferroptosis and Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment
Cancer immunotherapy has transformed oncological care by leveraging the immune system’s ability to target tumors. Despite its potential, challenges such as immune evasion and an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment limit its efficacy. Ferroptosis, a novel form of iron-dependent cell death, offers a unique mechanism to overcome these barriers by inducing immunogenic cell death, releasing signals that stimulate antitumor immune responses.
A New Approach: Nanoformulation CP
This study, led by Qunfang Yang and colleagues, aimed to combine ferroptosis and immunotherapy using a novel CP nanoformulation. The formulation integrates cannabinoid nanoparticles with the immunostimulant Poly(I:C), designed to reverse the tumor’s immunosuppressive environment and trigger robust immune activation. The research was published in Biomaterials on November 30, 2022.
Innovative Nanoformulation Design and Testing
The CP nanoformulation uses thermosensitive hydrogels to deliver cannabinoid nanoparticles and Poly(I:C) directly into tumors. This system enhances ferroptosis and amplifies immune responses by initiating T-cell activation and reversing immunosuppression. Its prolonged tumor retention ensures sustained therapeutic effects. The research involved rigorous in vivo testing, including subcutaneous tumor models and metastasis models in mice, to evaluate its efficacy in tumor suppression and immune activation.
Breakthrough Outcomes: Enhanced Tumor Suppression and Immune Activation
1. Tumor Suppression:
- In the B16F10 melanoma model, the CP-treated group showed a significant tumor weight reduction to 309 ± 25 mg compared to the saline group (1870 ± 190 mg) after 20 days of treatment.
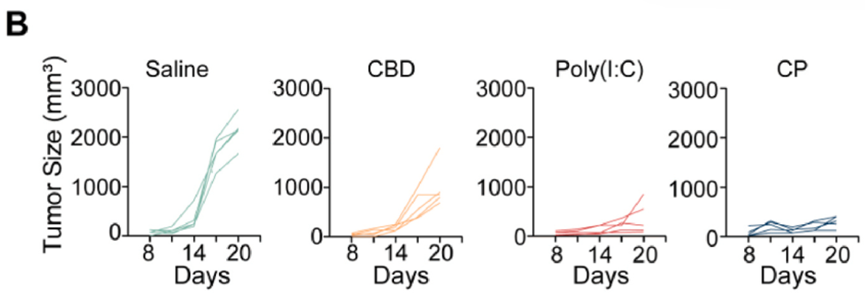
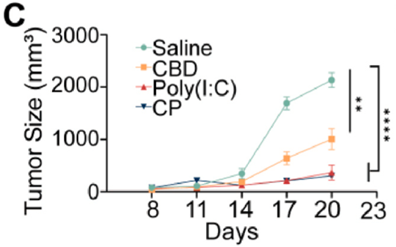
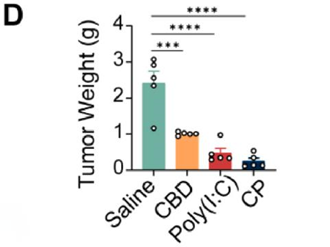
- Tumor volume was similarly reduced in CP-treated tumors to 320 ± 36 mm³ compared to 1943 ± 210 mm³ in the saline group.
2. Survival Outcomes:
- Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed 100% survival in CP-treated mice on day 25, compared to a 0% survival rate in the saline group.
3. Immune System Activation:
- CD8+ T Cell Infiltration: The percentage of CD8+ T cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs) increased significantly in the CP-treated group to 25.8 ± 1.7%, compared to 12.5 ± 0.8% in the saline group and 20.1 ± 1.5% in the Poly(I:C) group.
- Treg Reduction: Regulatory T cells (Tregs) in TDLNs decreased by approximately 2.27-fold in the CP-treated group compared to saline-treated controls.
4. Anti-metastatic Effects:
- In a lung metastasis model, CP treatment significantly reduced the metastatic tumor burden, with fewer nodules observed compared to saline, CBD NPs, and Poly(I:C) groups.
5. Innate Immune Activation:
- CP significantly enhanced innate immune responses by increasing the activity of neutrophils (4.02-fold), macrophages (2.02-fold), and natural killer cells (2.67-fold) compared to the saline group.
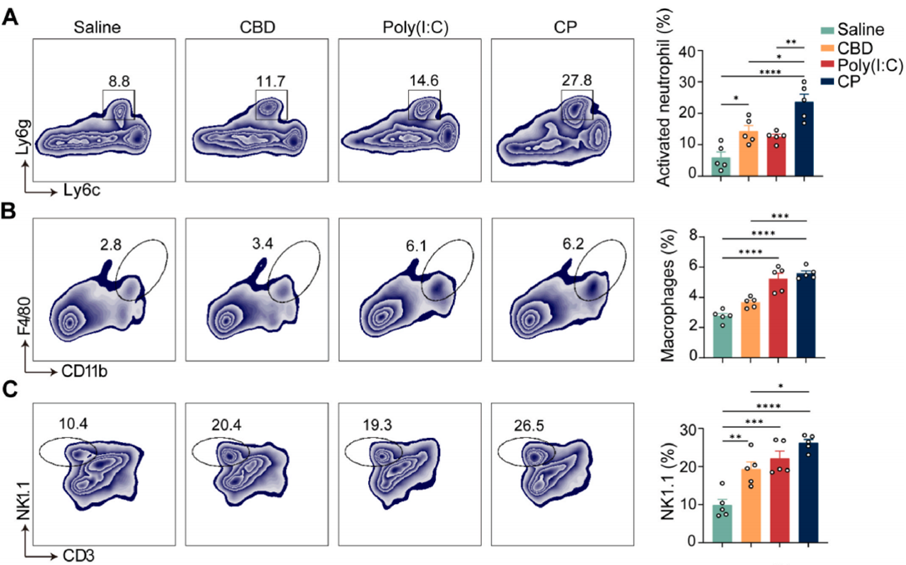
- Dendritic cell maturation in TDLNs was upregulated, as indicated by increased expression of MHC-II (12.29-fold), CD86 (2.82-fold), and MHC-I (1.6-fold) compared to the saline group.
6. Ferroptosis Induction:
- CP-treated tumors exhibited increased markers of ferroptosis, including elevated lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and decreased glutathione (GSH) content. The CP nanoformulation also showed mitochondrial shrinkage characteristic of ferroptosis in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images.
Toward a New Paradigm in Cancer Treatment
This study presents a novel nanoformulation, CP, which integrates ferroptosis induction with immunotherapy to enhance antitumor responses. The CP nanoformulation significantly suppresses tumor growth, reverses the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, and activates robust systemic immune responses. Preclinical experiments demonstrated its efficacy in reducing primary tumor progression and metastatic burden while improving survival outcomes in multiple cancer models. These findings underscore the potential of CP as a promising therapeutic strategy for broad-spectrum cancer treatment and highlight the innovative combination of ferroptosis and immunotherapy as a cornerstone for future cancer therapies.
Reference:
Yang, Qunfang, et al. “A nanoformulation for immunosuppression reversal and broad-spectrum self-amplifying antitumor ferroptosis-immunotherapy.” Biomaterials 292 (2023): 121936.
