High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), combined with innovative nanotechnology and immunotherapy, demonstrates remarkable potential in cancer treatment.
HIFU: Promise and Challenges
HIFU is a non-invasive cancer treatment technique that uses ultrasound waves to generate localized heat, effectively ablating tumor tissues. This method has been widely recognized for its precision, sparing surrounding healthy tissues and reducing recovery times compared to conventional surgical approaches. HIFU has demonstrated efficacy against a variety of cancers, including breast, liver, and pancreatic tumors.
Despite its promise, HIFU faces limitations that reduce its therapeutic impact. The energy delivered by the ultrasound waves diminishes as it penetrates deeper tissues, leading to incomplete ablation of tumors. Additionally, residual tumor cells left behind can promote recurrence or metastasis. These challenges underscore the urgent need for synergistic approaches that can overcome these barriers, improve tumor destruction, and achieve long-lasting outcomes.
A Novel Synergistic Strategy
In an effort to enhance the effectiveness of HIFU, the study explored a combination strategy that integrates immunotherapy and oxygen-releasing nanoparticles (M@P-SOP) with HIFU. The primary aim was to address two critical issues: inadequate energy delivery to tumors and the suppressive nature of the tumor microenvironment (TME), often characterized by hypoxia and immune evasion.
The research was conducted by a multidisciplinary team led by Dr. Pan Li at Chongqing Medical University and collaborators. The findings were published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer in 2023. The researchers propose that this three-pronged approach has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment by simultaneously amplifying HIFU efficacy, alleviating hypoxia, and triggering systemic immune responses.

Merging Nanotechnology with HIFU
Central to this approach is the development of M@P-SOP nanoparticles, designed with a cancer cell membrane coating for enhanced tumor targeting. These nanoparticles are multifunctional, carrying oxygen to relieve tumor hypoxia while amplifying the energy deposition of HIFU. They also incorporate imaging capabilities, including ultrasound, photoacoustic, and MRI, to guide and monitor treatment in real time.
The experimental methodology involved preclinical cancer models, where researchers evaluated the combined effects of HIFU, M@P-SOP, and PD-L1 checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. The study employed advanced imaging modalities to track nanoparticle distribution and measure treatment responses, highlighting the precision and efficiency of this novel therapeutic platform.
Results
- Enhanced Tumor Ablation
The combination of HIFU and M@P-SOP nanoparticles significantly increased the tumor necrotic volume by approximately 75% compared to HIFU alone. The energy efficiency factor (EEF) demonstrated notable improvement, requiring 35% less ultrasound energy to achieve comparable therapeutic effects.
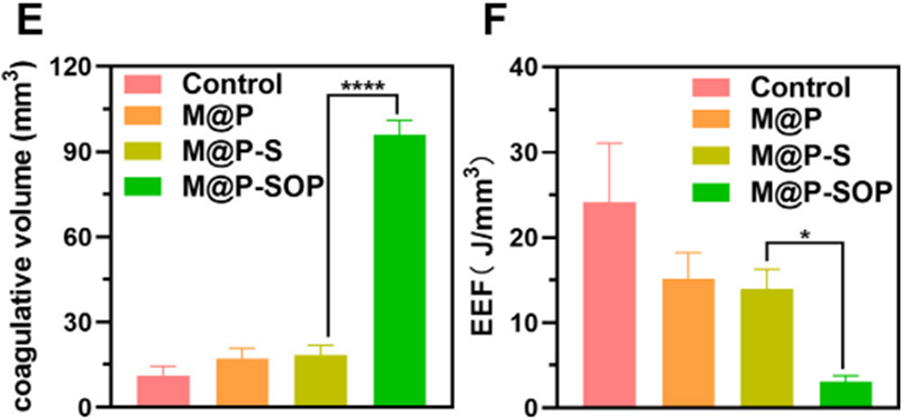
- Improved Tumor Oxygenation
M@P-SOP nanoparticles effectively alleviated tumor hypoxia, with HIF-1α levels reduced by 50% in treated tumors. The nanoparticles released nearly 100% of their oxygen payload within 30 minutes of HIFU irradiation, creating a more favorable tumor microenvironment (TME) for immune response activation.
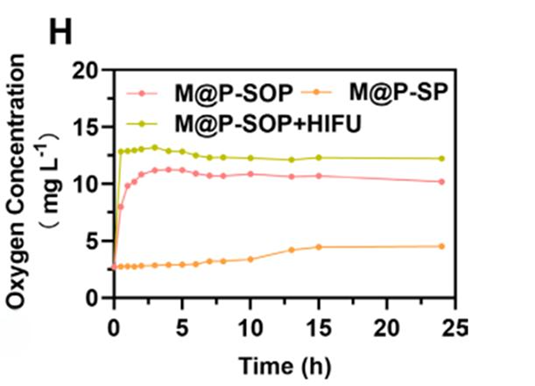
- Robust Immune Activation
The combination therapy enhanced systemic antitumor immunity by increasing CD8+ T cell infiltration nearly 2.5 times and promoting dendritic cell (DC) maturation in tumor-draining lymph nodes by 70%. Additionally, it repolarized macrophages in the TME, with M1 macrophage levels rising by 40% and M2 macrophage levels reduced by 24%.
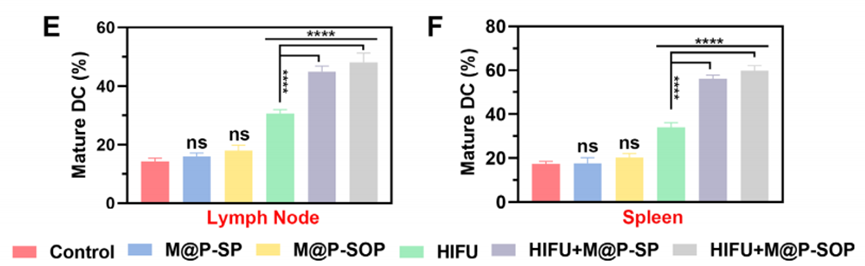
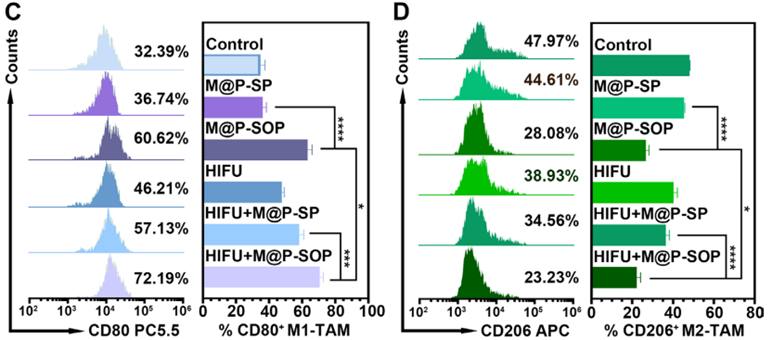
Quantitative data from the experiments revealed enhanced tumor suppression rates and significant improvements in immune activation metrics. The synergy of HIFU, M@P-SOP, and PD-L1 immunotherapy demonstrated superior efficacy in targeting both primary and distant metastatic tumors.
Study Significance
This innovative strategy highlights a path forward in the battle against cancer. By integrating HIFU, oxygen delivery, and immunotherapy, researchers have developed a versatile approach with strong potential for clinical application across various solid tumors. With HIFU already established in clinical practice, this study opens avenues for enhanced therapeutic efficacy and improved patient outcomes.
Reference:
Tang, Rui, et al. “Novel combination strategy of high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) and checkpoint blockade boosted by bioinspired and oxygen-supplied nanoprobe for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy.” Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer 11.1 (2023).
