A study highlights the potential of combining Etoricoxib and Cannabidiol (CBD) with advanced nanoparticle technology to combat glioblastoma, a devastating brain cancer.
Understanding Glioblastoma and Current Challenges
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive primary malignant tumor of the central nervous system, representing 57% of gliomas. Despite multimodal treatments like surgery, radiotherapy, and temozolomide chemotherapy, the prognosis remains grim, with a median survival of less than two years. Its aggressive nature and resistance to conventional therapies necessitate innovative treatment approaches.
Research has shown that inflammation plays a significant role in GBM progression, linking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Etoricoxib and natural compounds like CBD as promising candidates to improve therapeutic outcomes. However, effective delivery through the blood-brain barrier remains a significant hurdle.
Research Aim and Objectives: Exploring a Novel Treatment Avenue
This study, led by Joanna Kuźmińska and colleagues from Poznan University of Medical Sciences, aimed to investigate the synergistic antitumor effects of Etoricoxib and CBD, encapsulated in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)-based nanoparticles. The research was published in Pharmaceutics in August 2023, underscoring its contribution to addressing delivery challenges and enhancing drug efficacy in GBM treatment.
Innovative Experimental Approaches
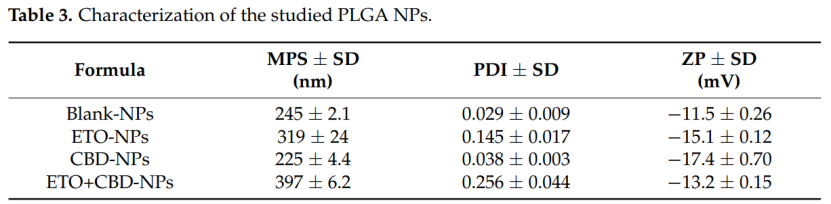
The researchers developed PLGA nanoparticles using an emulsification-solvent evaporation method. These nanoparticles were characterized by their spherical shape, mean particle size of 397 nm, and entrapment efficiencies of 78.43% for CBD and 10.94% for Etoricoxib. Advanced analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography and scanning electron microscopy were employed to ensure quality and consistency.
The antitumor effects of the Etoricoxib-CBD combination were tested on T98G and U-138 MG GBM cell lines using MTT viability assays, cell cycle distribution analysis, and apoptosis assays. The goal was to assess both individual and combined drug efficacy and determine the nanoparticles’ potential in overcoming drug delivery barriers.
Promising Outcomes for GBM Therapy
Results showed that the combination of Etoricoxib and CBD significantly reduced GBM cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. For example, at 25 μM concentrations of both drugs, apoptosis rates in the T98G cell line reached 31.89%—a marked improvement over individual drug effects. The combination also induced notable cell cycle arrest and increased early and late apoptosis in GBM cells.
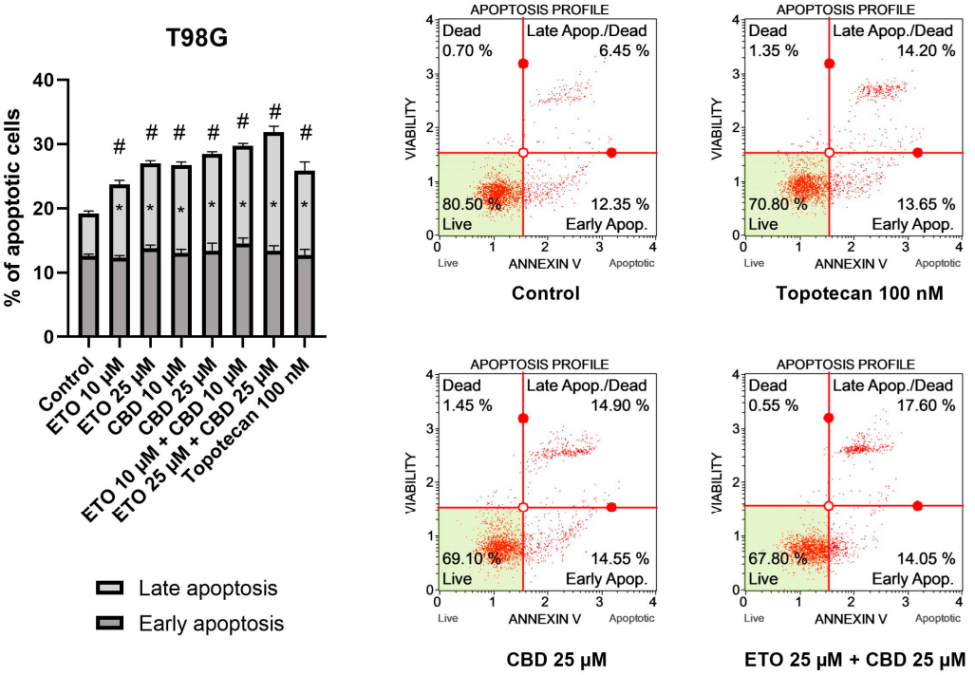
PLGA nanoparticles enhanced the therapeutic effects by facilitating efficient drug delivery. Compared to free drugs, nanoparticle-encapsulated drugs demonstrated higher efficacy in reducing cell viability and promoting apoptosis. The nanoparticles also showed favorable physical properties, such as a polydispersity index of 0.256 and a zeta potential of -13.2 mV, making them suitable for brain delivery.
Significance of Findings for Glioblastoma Treatment
This research investigated the synergistic antitumor effects of Etoricoxib and Cannabidiol (CBD) in glioblastoma (GBM) treatment and developed a nanoparticle-based delivery system using PLGA. The study demonstrated that the combination of Etoricoxib and CBD significantly reduced GBM cell viability and enhanced apoptosis in in vitro models.
The developed PLGA nanoparticles effectively encapsulated both drugs, showing favorable physicochemical properties such as controlled size, stability, and drug release profiles. The results highlight the potential of this drug combination and nanoparticle system in addressing delivery challenges and improving antitumor efficacy in GBM cell lines. These findings provide data that could inform future studies on GBM therapeutic strategies.
Reference:
Kuźmińska, Joanna, et al. “Etoricoxib-Cannabidiol Combo: Potential Role in Glioblastoma Treatment and Development of PLGA-Based Nanoparticles.” Pharmaceutics 15.8 (2023): 2104.
