Editor: Nina
Scientists develop a transdermal drug delivery system combining dissolving microneedles with nanosuspension and co-grinding techniques to improve the solubility and delivery of ketoprofen.
Key Preview
Research Question
The study addresses the challenge of delivering ketoprofen transdermally while overcoming its low solubility and potential gastric irritation associated with oral administration. The primary research question focuses on whether combining dissolving microneedles (DMN) with nanosuspension (NS) and co-grinding (CG) techniques can enhance the transdermal delivery of ketoprofen.
Research Design and Strategy
The research employs a systematic approach involving the formulation of DMN utilizing both nanosuspension and co-grinding methods. By evaluating the dissolution profiles, physical and chemical properties, and in vitro permeation studies, the study aims to identify the most effective formulation for transdermal delivery.
Method
The method included creating ketoprofen-loaded nanosuspensions with varying concentrations of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and co-grinding ketoprofen with PVA or poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP). The formulations were characterized, followed by in vitro permeation studies using Franz diffusion cells.
Key Results
The most promising formulations identified were F5-MN-NS and F11-MN-CG, yielding cumulative drug permeation of 3.88 ± 0.46 µg and 8.73 ± 1.40 µg after 24 hours, respectively. These results indicate that combining DMN with nanosuspension or co-grinding significantly enhances ketoprofen’s transdermal delivery.
Significance of the Research
This research is significant as it presents a novel strategy for improving the transdermal delivery of ketoprofen, addressing the limitations associated with its oral administration. The findings suggest potential applications in pain management therapies, particularly for patients suffering from osteoarthritis.
Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It is one of the most prevalent forms of arthritis, affecting millions of individuals worldwide, particularly the elderly. The condition significantly impacts quality of life and can lead to disabilities, making effective pain management a critical aspect of treatment.
Traditionally, OA is managed using oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ketoprofen, which help alleviate pain and inflammation. While these medications can be effective, their oral administration poses several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for gastrointestinal irritation and bleeding, especially with long-term use. Additionally, orally administered drugs often undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver, which can reduce their bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness.
These challenges result in inadequate pain relief for many patients and may require higher doses, further increasing the risk of side effects. Moreover, the low solubility of certain NSAIDs can hinder their absorption and efficacy, complicating treatment regimens.
To address these limitations, innovative drug delivery strategies are being explored. One promising approach is the use of dissolving microneedles (DMN) combined with nanosuspension and co-grinding techniques. This method aims to enhance the transdermal delivery of poorly soluble drugs like ketoprofen, allowing for direct administration into the systemic circulation while bypassing gastrointestinal complications. By improving solubility and bioavailability, this innovative strategy has the potential to provide effective pain relief for patients with osteoarthritis, offering a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional oral therapies.
Research Team and Aim
The research team was led by Delly Ramadon, a prominent researcher from the Faculty of Pharmacy at Universitas Indonesia. The study was conducted from 2022 to 2023, in collaboration with colleagues from both Universitas Indonesia and Queen’s University Belfast. The research was titled “Combination of Dissolving Microneedles with Nanosuspension and Co-Grinding for Transdermal Delivery of Ketoprofen” and was published in the journal Pharmaceuticals.
The aim of the research, as articulated by the lead researcher, was to develop and optimize dissolving microneedle formulations containing ketoprofen, enhancing its solubility and transdermal delivery potential. This innovative approach seeks to overcome the limitations associated with traditional oral administration of the drug, ultimately improving pain management outcomes for patients suffering from osteoarthritis.
Experimental Process
Primary Technique
The primary technique employed in this study was the formulation of dissolving microneedles (DMN) combined with nanosuspension (NS) and co-grinding (CG) methods for the transdermal delivery of ketoprofen. This method allows for enhanced solubility and bioavailability of the drug while minimizing gastrointestinal irritation associated with oral administration.
Key Steps of Each Experiment
- Formulation of Nanosuspension:
- Preparation: Ketoprofen was dissolved in varying concentrations of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) (0.5%, 1%, and 2%) in distilled water.
- Ultrasonication: The mixture was subjected to ultrasonication for 5 minutes to create nanosuspensions, effectively reducing particle size and enhancing solubility.
- Characterization: The resulting nanosuspensions were characterized by measuring particle size and zeta potential to assess stability.
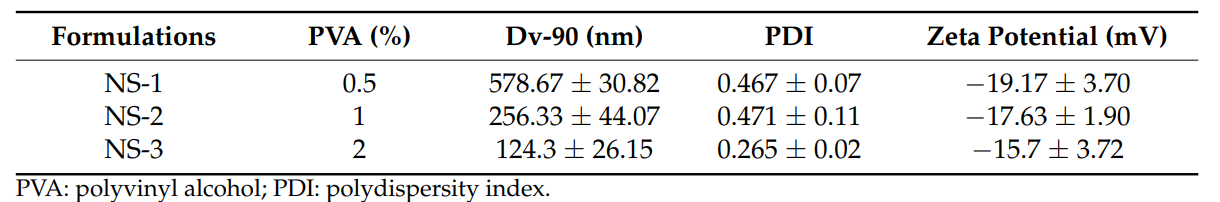
Table 1. Particle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential of Nanosuspension Formulations (n = 3, mean ± SD).
- Co-Grinding:
- Grinding Process: Ketoprofen was co-ground with PVA or poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) at different drug-polymer ratios (e.g., 3:1, 5:1, 10:1) using a mortar and pestle.
- Dissolution Profile Assessment: The co-ground samples were then analyzed for their dissolution profiles to evaluate improvements in solubility compared to pure ketoprofen.
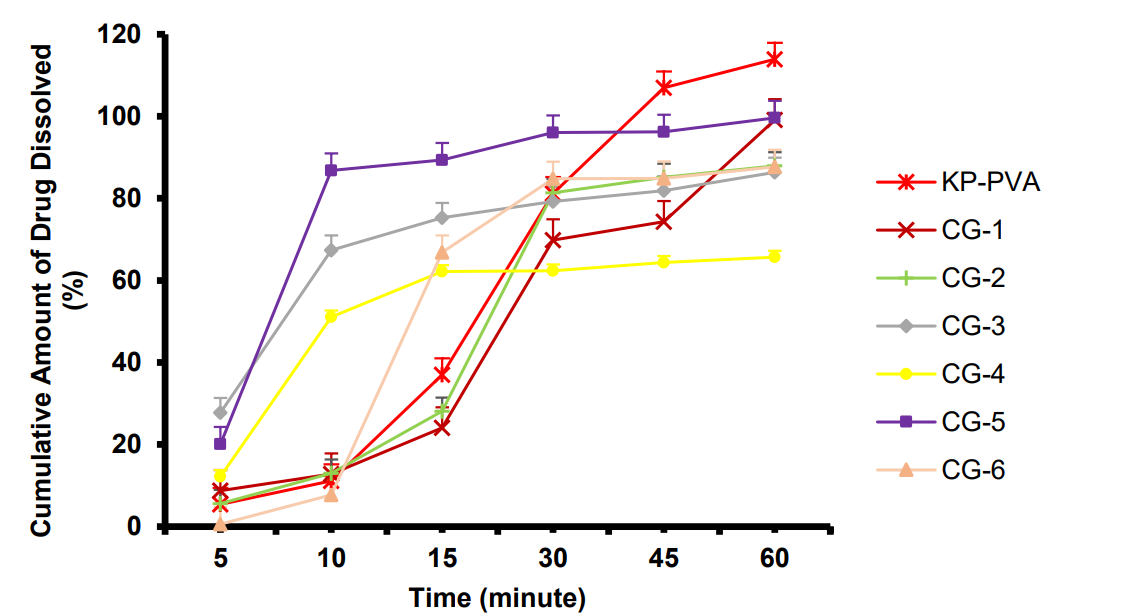
Figure 1. Dissolution profile curve of Co-grinded ketoprofen (n = 3, mean + SD, p > 0.05)
- Microneedle Fabrication:
- Molding Technique: The most promising formulations from the nanosuspension and co-grinding processes were poured into silicone molds designed for DMN, allowing for the formation of microneedles.
- Drying Process: The molds were subjected to a positive pressure environment to facilitate efficient drying of the microneedles.
- In Vitro Permeation Studies:
- Setup: Franz diffusion cells were used, with rat skin as the membrane to simulate transdermal delivery.
- Sampling: The cumulative drug permeated was collected over 24 hours at defined intervals to measure the effectiveness of the DMN formulations.
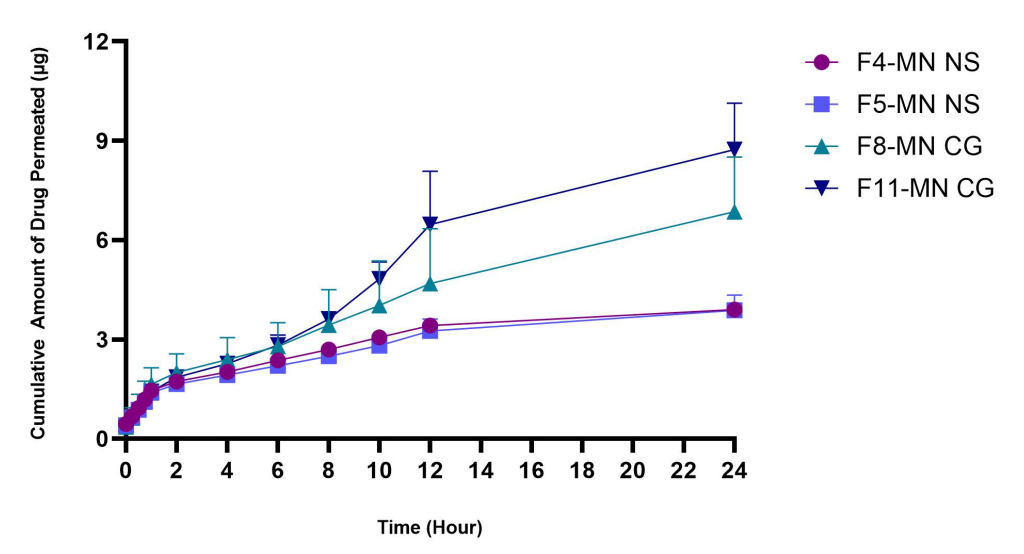
Figure 2. The cumulative amount of drug permeated in vitro using Franz diffusion cells for 24 h from DMN loaded with nanosuspension and Co-grinded ketoprofen (n = 3, mean ± SD, p > 0.05).
Data Collection and Analysis
Data were collected through a series of quantitative assays. For the nanosuspension and co-grinding formulations, UV-Vis spectrophotometry was utilized to measure drug concentration and dissolution rates. In the permeation studies, the cumulative amount of drug permeated was analyzed using statistical methods to assess differences between formulations, ensuring rigor in the results.
Novel Aspects
This study introduced a combined approach of using DMN with nanosuspension and co-grinding techniques, which is a significant advancement over traditional nano-delivery systems. The novel aspect is the integration of these methods to enhance the solubility and transdermal delivery of poorly soluble drugs like ketoprofen. This dual approach not only improves drug bioavailability but also reduces the risk of gastrointestinal side effects, presenting a more patient-friendly alternative for pain management therapies.
Conclusion
The successful development of the drug delivery system combining dissolving microneedles with nanosuspension and co-grinding techniques was achieved through a systematic and innovative approach. By formulating ketoprofen into these advanced delivery systems, the research effectively enhanced the drug’s solubility and bioavailability, addressing the significant challenges associated with traditional oral administration.
The study highlighted that the most promising formulations, specifically F5-MN-NS and F11-MN-CG, achieved cumulative drug permeation values of 3.88 ± 0.46 µg and 8.73 ± 1.40 µg after 24 hours, respectively. These results underscore the effectiveness of the combined DMN approach in significantly improving transdermal delivery of ketoprofen. Overall, the findings suggest that this innovative delivery system could offer a safer and more efficient alternative for pain management in patients with osteoarthritis, paving the way for future research and clinical applications.
Reference
Ramadon, Delly, et al. “Combination of dissolving microneedles with nanosuspension and co-grinding for transdermal delivery of ketoprofen.” Pharmaceuticals 16.3 (2023): 378.
