Editor: Sarah
A recent study has introduced an innovative drug delivery system designed to improve the efficacy of chemotherapy for one of the most challenging forms of breast cancer: Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Researchers from multiple institutions have developed a targeted nanoparticle system using thiolated chitosan to deliver the chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a widely used drug in cancer treatment. This new system shows promise for enhancing the therapeutic effectiveness of 5-FU while reducing its harmful effects on healthy tissues.
The Challenge of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) is notoriously difficult to treat due to the absence of the three primary receptors commonly targeted by standard breast cancer treatments. This lack of receptors makes TNBC resistant to therapies like hormone treatments and HER2-targeted drugs. Consequently, available treatments often come with severe side effects, including nausea, hair loss, and fatigue. This study aims to tackle the issue of more effective targeting of cancer cells, ensuring better delivery of chemotherapy agents directly to the tumors.
Innovative drug delivery systems
While previous research has highlighted nanoparticles as effective carriers for drug delivery, challenges such as poor drug targeting and unwanted side effects have persisted. This study makes a significant advancement by utilizing hyaluronic acid (HA)-coated thiolated chitosan nanoparticles, which specifically target the CD44 receptors, commonly overexpressed on the surface of cancer cells, particularly in TNBC. The nanoparticles’ surface modification ensures they selectively bind to these receptors, facilitating the direct delivery of the drug to cancerous cells.
Contributions and Key Findings:
- Targeted Delivery with HA-Coated Nanoparticles: The study introduced a novel nanoparticle system utilizing hyaluronic acid (HA) and thiolated chitosan. The HA modification ensures the nanoparticles specifically target CD44 receptors, which are overexpressed in TNBC cells, enabling more efficient and precise drug delivery.
- Enhanced Cytotoxicity of 5-FU: The nanoparticles significantly enhanced the cytotoxic effects of 5-FU against TNBC cells (MDA-MB-231) when compared to conventional drug delivery methods. The nanoparticles demonstrated increased drug encapsulation efficiency and a sustained release profile, indicating potential for prolonged therapeutic effects.
- Safety Profile: When tested on normal breast cells (MCF-10A), the nanoparticle formulation exhibited significantly lower cytotoxicity, underscoring the targeted nature of the treatment and its potential to minimize side effects on healthy tissues.
- Stable and Effective Nanoparticle Formulation: Using the ionic gelation method, the nanoparticles were synthesized and characterized using various techniques, including SEM, TEM, FTIR, and XRD. These analyses confirmed that the nanoparticles were of optimal size and structure for efficient drug delivery, with a favorable particle size of less than 300 nm.
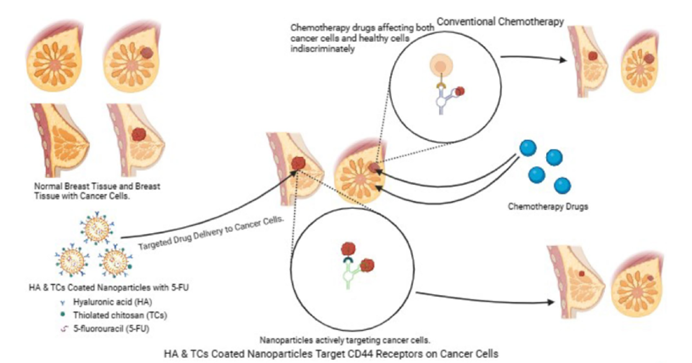
Figure 1: Schematic illustration of targeted delivery of HA-coated 5-FU in TCs-NPs formulation for the treatment of breast cancer compared to concentional chemotherapeutic drugs.
- In Vitro Efficacy: The nanoparticles showed a promising release pattern consistent with the basic diffusion model, and in vitro testing on TNBC cells revealed significantly improved cytotoxicity compared to the raw 5-FU, validating the effectiveness of the new system in targeting cancer cells.
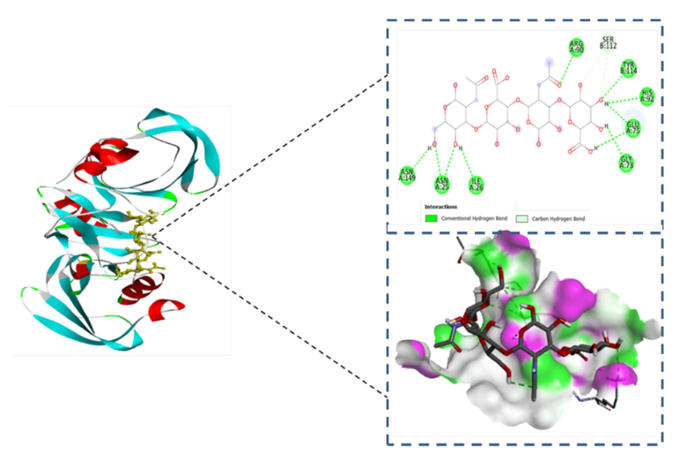
Figure 2: 2d and 3d interactions of hyaluronic acid with CD44 macromolecule.
- Potential for Broader Application: Although the results are promising in vitro, further in vivo studies are necessary to fully validate the nanoparticles’ effectiveness and to explore the potential for clinical applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of HA-coated thiolated chitosan nanoparticles for 5-FU delivery represents an important advancement in cancer treatment. This system holds promise for improving the therapeutic effectiveness of 5-FU while reducing the toxicity associated with traditional chemotherapy. The success of this drug delivery system in enhancing the targeted delivery of 5-FU provides hope for more effective and less toxic treatment options for patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Additionally, this approach may have applications for other cancer types, potentially altering the landscape of cancer therapy.
Reference
Anjum, Sadia, et al. “Enhancing Therapeutic Efficacy: Sustained Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) via Thiolated Chitosan Nanoparticles Targeting CD44 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.” Scientific Reports, vol. 14, no. 11431, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55900-1.
