Editor: Sarah
A recent study by Zhou et al. (2023) has advanced our understanding of how circular RNA (circRNA) influences the progression of breast cancer and introduced a promising RNA-based therapeutic approach.
Breast Cancer and the circPAPD4 Mechanism
Breast cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, fueling the ongoing search for novel therapeutic strategies. The study by Zhou and colleagues investigates the role of circPAPD4, a specific type of circular RNA, in regulating tumor progression in breast cancer. The researchers uncovered how circPAPD4 interacts with several key molecules, including miR-1269a, CREBZF, STAT3, and ADAR1, through a complex feedback loop.
One of the notable findings of the study was the application of nanoparticles to deliver CREBZF mRNA directly into cancer cells, which resulted in significant suppression of breast cancer progression. This RNA-based therapy could provide an alternative to traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation, presenting a potential new avenue for cancer treatment.
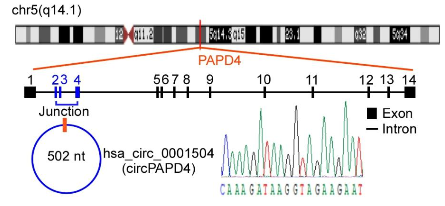
Schematic representation of the formation of circPAPD4 through back-splicing, illustrating the structural characteristics of this circular RNA.
CircPAPD4’s Role in Tumor Suppression
Zhou et al. demonstrate that circPAPD4 is typically downregulated in breast cancer tissues, and its reduced expression is linked to poorer patient prognosis. The study revealed that circPAPD4 helps to suppress tumor growth by inhibiting cell proliferation and encouraging apoptosis (programmed cell death). This effect is mediated through the binding of circPAPD4 to miR-1269a, which in turn regulates the expression of CREBZF, a transcription factor.
A key discovery in this study is the identification of a novel positive feedback loop in which CREBZF inhibits STAT3 dimerization, thereby promoting circPAPD4 expression. This feedback loop not only amplifies the tumor-suppressive effects of circPAPD4 but also sets the stage for further research into its potential as both a biomarker and therapeutic target.
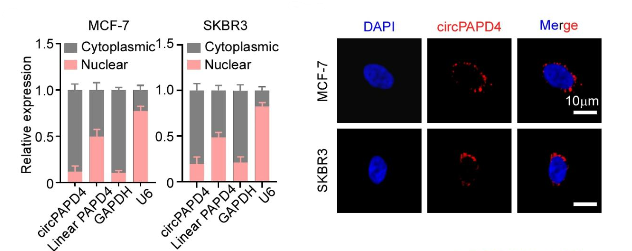
Distribution of circPAPD4 within the cytoplasm of breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and SKBR-3) as observed through subcellular fractionation and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assays.
Innovative Nanoparticle Therapy
In a promising development, the researchers successfully used nanoparticles to deliver CREBZF mRNA into CREBZF-null breast cancer cells. This method restored CREBZF expression and led to a significant reduction in tumor growth in xenograft models, illustrating a novel approach to targeting cancer at the molecular level.
The research team employed a range of advanced techniques, including RNA pull-down assays, luciferase reporter assays, and xenograft experiments in mice, to validate the role of circPAPD4 in breast cancer. These findings underscore the potential of nanoparticle-based RNA delivery systems to manipulate gene expression in cancer cells, offering a safer and more effective alternative to conventional therapies.
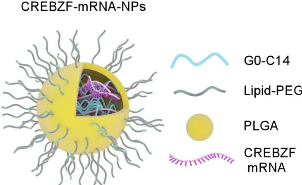
Schematic diagram of CREBZF mRNA nanoparticles (CREBZF-mRNA-NPs), which consist of PLGA polymers and lipid-PEG components designed for targeted delivery of CREBZF mRNA.
Contributions and Key Findings
- Identification of circPAPD4: This study identified circPAPD4 as a crucial player in the regulation of breast cancer progression. The circRNA was found to be downregulated in breast cancer tissues, and its expression correlated negatively with poor prognosis markers, such as tumor size and advanced stages of the disease.
- Tumor Suppressive Functions of circPAPD4: The study showed that circPAPD4 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. This function was primarily attributed to its ability to bind to miR-1269a, a microRNA that negatively regulates CREBZF, a key transcription factor involved in tumor growth.
- The circPAPD4/miR-1269a/CREBZF/STAT3/ADAR1 Feedback Loop: A novel positive feedback loop was discovered involving circPAPD4, miR-1269a, CREBZF, STAT3, and ADAR1. CREBZF inhibits STAT3 dimerization, leading to increased circPAPD4 expression, which in turn amplifies the tumor-suppressive effects of the circRNA.
- RNA-based Nanoparticle Therapy: The use of nanoparticles to deliver CREBZF mRNA to cancer cells marked a significant step forward in RNA-based cancer therapies. The method successfully reintroduced CREBZF expression into CREBZF-null cells, reducing tumor growth and providing a potential new treatment modality for breast cancer.
- Preliminary In Vivo Results: In animal models, the application of CREBZF-mRNA-NPs showed promising results, significantly suppressing tumor growth and inducing apoptosis without noticeable side effects. These findings suggest that nanoparticle-based RNA therapies could offer a safer, more targeted approach compared to traditional treatments.
Implications for Future Cancer Treatment
The findings from this study hold significant potential for advancing cancer treatment strategies. By targeting the circPAPD4/miR-1269a/CREBZF/STAT3/ADAR1 feedback loop, researchers may develop more precise and effective RNA-based therapies for various types of cancer. These therapies could offer patients a better quality of life with fewer side effects compared to conventional treatments.
Furthermore, the study contributes to the growing body of knowledge on the role of circular RNAs in cancer biology, particularly their ability to regulate gene expression through competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) interactions. This work represents one of the first clear mechanistic links between circPAPD4 and breast cancer progression, paving the way for further investigations into its potential as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target.
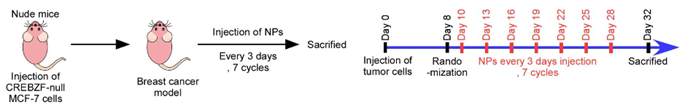
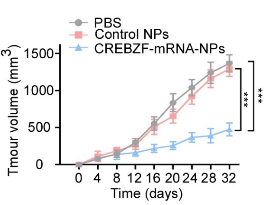
Tumor growth suppression in xenograft mice treated with CREBZF-mRNA-NPs, highlighting the efficacy of RNA-based therapy in reducing tumor size compared to control groups.
A New Frontier in Cancer Therapy
This study represents a significant advancement in our understanding of breast cancer and the potential of RNA-based therapies. The successful application of these innovative therapeutic strategies opens up new possibilities for treating breast cancer and other malignancies. With continued research and development, RNA therapies like those targeting circPAPD4 could become integral components of future cancer treatment regimens.
Reference
Zhou, Boxuan, et al. “New Study Illuminates the Role of Circular RNA in Breast Cancer and Presents RNA-Based Therapeutic Strategy.” Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, vol. 42, no. 138, 2023
