Editor: Nina
This study demonstrates that a curcumin-resveratrol nanoemulsion effectively mitigates hyperammonemia and its associated hepatic and cerebral dysfunctions induced by a protein-deficient diet in juvenile rats, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic strategy for managing hyperammonemia.
Key Preview
Research Question
The study investigates the efficacy of a curcumin-resveratrol nanoemulsion formulation in counteracting hyperammonemia induced by a protein-deficient diet (PDD) in male albino rats.
Research Design and Strategy
The researchers employed an experimental design involving male Wistar albino rats divided into different groups. Each group received varying doses of the nanoemulsion or control treatments over 15 days after a 75-day PDD regimen.
Method
The method involved preparing a nanoemulsion of curcumin and resveratrol, which was administered to rats. Key metrics such as hepatic and brain ammonia levels, serum liver enzymes, and neurotransmitter levels were measured.
Key Results
The nanoemulsion significantly reduced ammonia levels in the liver and brain, normalized serum ALT and AST levels, and improved monoamine neurotransmitter levels, indicating its effectiveness against PDD-induced hyperammonemia.
Significance of the Research
This research highlights a novel approach using a combined nano-formulation to enhance the bioavailability of curcumin and resveratrol, potentially offering a therapeutic strategy for managing hyperammonemia.
Introduction
The prevalence of hyperammonemia, characterized by elevated ammonia levels that can lead to severe neurological dysfunction, is a pressing concern in medical research. Previous studies have linked malnutrition and low protein intake to increased risks of hyperammonemia, which can particularly affect pediatric populations. Curcumin and resveratrol, two well-researched polyphenols, have demonstrated protective effects against hepatic and cerebral injuries but are constrained by their low bioavailability. This study explores an innovative solution: a novel nanoemulsion formulation combining curcumin and resveratrol to effectively counteract the adverse effects of PDD-induced hyperammonemia.
Research Team and Objective
The research was conducted by a team led by Prof. Dr. Maha Nasr, along with Ass. Prof. Dr. Rania F. Ahmed and Ass. Prof. Dr. Omar A.H. Ahmed-Farid, from Ain Shams University and the National Research Centre in Egypt. Published in Metabolic Brain Disease, the study titled “Curcumin-resveratrol nano-formulation counteracting hyperammonemia in rats” aims to examine the therapeutic potential of this combined formulation in ameliorating the hepatic and cerebral complications resulting from hyperammonemia.
Experimental Process
The experimental process of this study consisted of several key procedures designed to investigate the efficacy of a curcumin-resveratrol nanoemulsion in counteracting hyperammonemia induced by a protein-deficient diet (PDD) in male albino rats. Below is an outline of the key experimental procedures, including their steps, results, significance, and innovations.
Preparation of Nanoemulsions
Key Steps:
- Curcumin and resveratrol were individually dissolved in Labrafac Lipophile oil (10% w/v) and Cremophor RH surfactant (10% w/v). – The oil-surfactant mixture was gradually added to a magnetically stirred aqueous phase at room temperature to form nanoemulsions.
- The resulting emulsions were characterized for particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential using a Zetasizer device.
Results and Key Data: - The average particle sizes were 136 nm for curcumin, 128 nm for resveratrol, and 135 nm for the combined formulation, indicating successful nanoemulsion formation.
- Polydispersity indices (≤ 0.39) suggested uniform particle distribution, and zeta potentials (ranging from -15.92 to -18.93 mV) indicated stability.
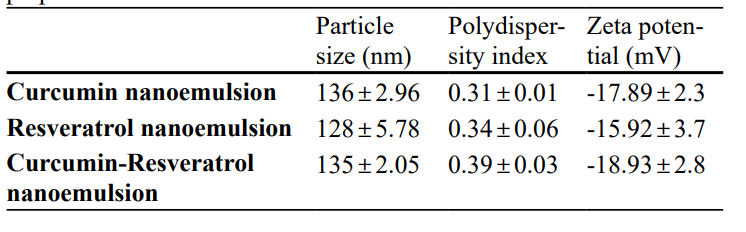
Table 1. Particle size, polydispersity index and zeta potential of the prepared nanoemulsions
Significance of the Result:
- The successful preparation of stable nanoemulsions enhances the bioavailability of curcumin and resveratrol, making them more effective in biological applications.
Key Innovations: - The spontaneous emulsification method used here is a novel approach that improves the solubility and absorption of poorly water-soluble compounds like curcumin and resveratrol.
Animal Model Selection
Key Steps:
- Male Wistar albino juvenile rats (60-70 grams) were acclimatized for seven days prior to the study. – The rats were divided into eight groups (n = 16) for controlled experimental conditions.
Results and Key Data: - Groups included a normal control (fed a standard diet) and seven PDD groups receiving varying doses of the nanoemulsion or control treatments.
Significance of the Result: - The use of a consistent animal model allows for reliable comparisons between treatment groups, reinforcing the validity of the findings.
Key Innovations: - This study utilizes a long acclimatization period, which is critical for minimizing stress-related variables that could confound the results.
Dietary Intervention and Treatment Administration
Key Steps:
- All rats were subjected to a PDD consisting of shelled corn grains for 75 days to induce hyperammonemia.
- Starting from day 61, treatment groups received daily oral doses of either curcumin, resveratrol, or a combination of both in nanoemulsion form for 15 days.
Results and Key Data: - The PDD resulted in a significant increase in serum ALT and AST levels, indicating hepatic dysfunction.
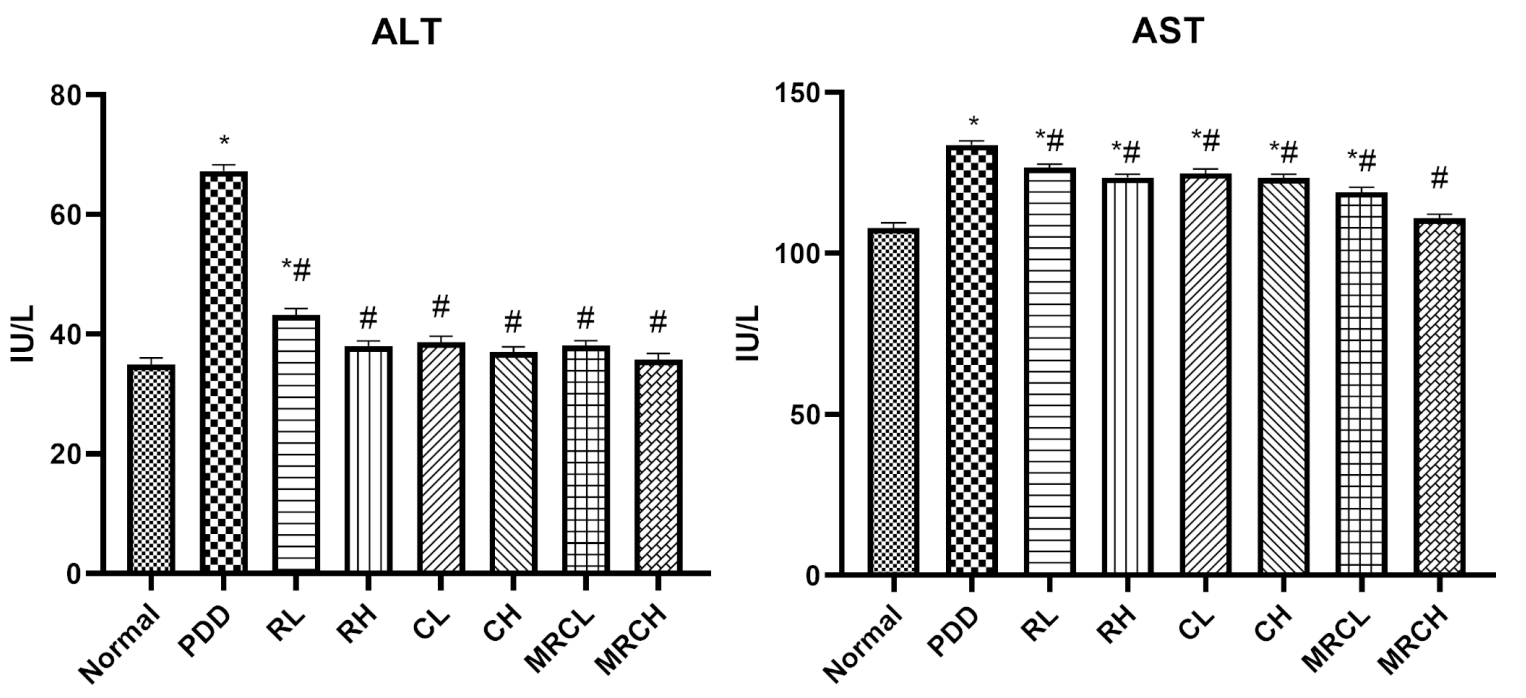
Figure 1. Impact of different treatments on serum hepatic enzymes ALT and AST. * Signiffcance vs. normal, # signiffcance vs. PDD control
Significance of the Result:
- Establishing a hyperammonemic condition is crucial for evaluating the protective effects of the nanoemulsion on liver function and ammonia levels.
Key Innovations: - The combined administration of curcumin and resveratrol represents a novel therapeutic strategy aimed at maximizing their synergistic effects against hyperammonemia.
Biochemical Analysis of Blood and Tissue Samples
Key Steps:
- After the treatment period, blood samples were collected under phenobarbital anesthesia for serum ALT and AST measurements.
- Liver and brain tissues were harvested for ammonia, nitric oxide (NOx), oxidative stress markers (8-OHdG), and neurotransmitter levels (serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and glutamate).
Results and Key Data: - Nanoemulsion treatments significantly reduced hepatic and brain ammonia levels by up to 81.17% and normalized serum enzyme levels, demonstrating effective hepatic protection.
- Enhanced neurotransmitter levels and reduced oxidative stress markers were observed, indicating improved neuronal function.
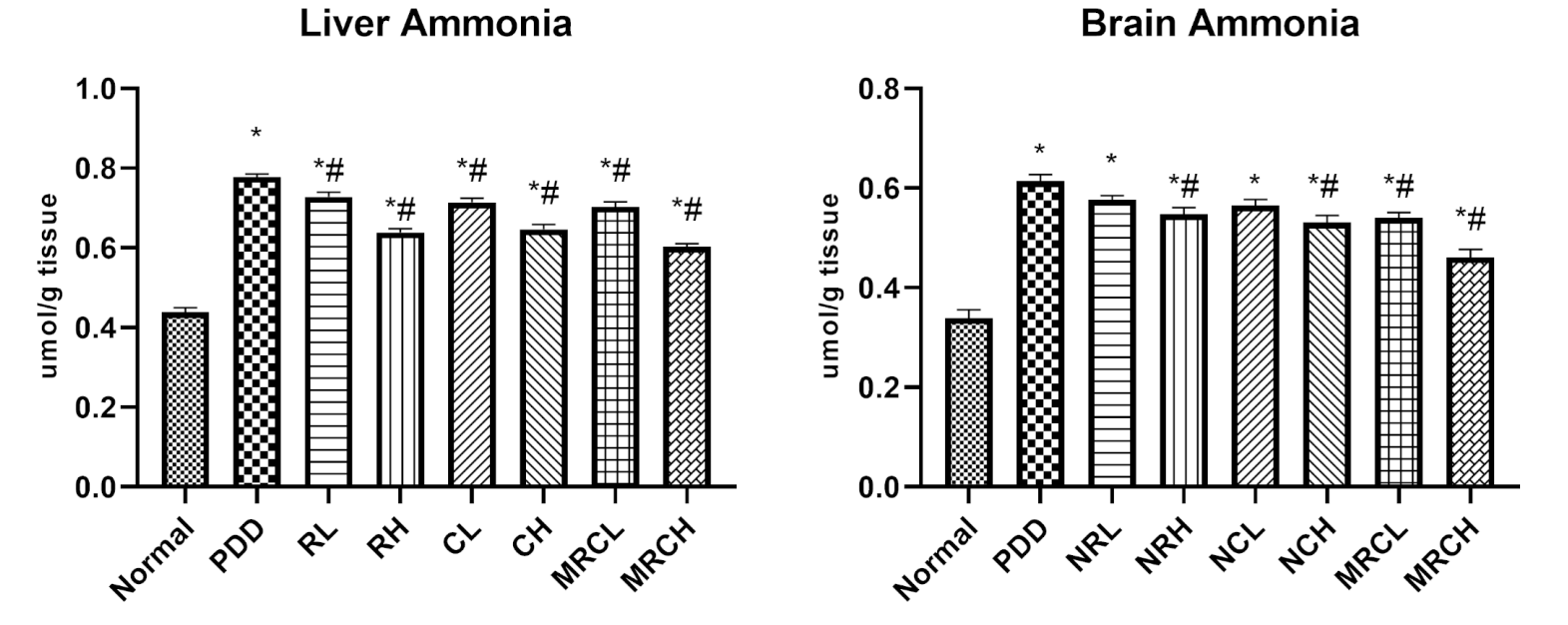
Figure 2. Impact of different treatments on hepatic and brain ammonia levels. * Signiffcance vs. normal, # signiffcance vs. PDD control
Significance of the Result:
- These results confirm the potential of the curcumin-resveratrol nanoemulsion to mitigate the hepatotoxic effects associated with hyperammonemia and restore neurotransmitter balance.
Key Innovations: - The comprehensive biochemical profiling of both blood and tissue samples provides a multifaceted view of the therapeutic effects, illustrating the nanoemulsion’s impact on both hepatic and cerebral health.
Statistical Analysis
Key Steps:
- Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test to determine the significance of treatment effects.
- Correlation studies were conducted to identify relationships between ammonia levels and other biochemical parameters.
Results and Key Data: - Statistical analyses revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) in key parameters across treatment groups, supporting the therapeutic efficacy of the nanoemulsions.
Significance of the Result: - Robust statistical validation ensures that the observed effects are not due to chance, reinforcing the credibility of the findings.
Key Innovations: - The incorporation of correlation studies enhances the understanding of the interactions between ammonia levels and metabolic markers, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms of treatment effects.
Conclusion
The findings of this study indicate that the curcumin-resveratrol nanoemulsion effectively mitigated the adverse effects of hyperammonemia induced by a protein-deficient diet in juvenile rats. This research opens avenues for potential therapeutic strategies targeting hyperammonemia, particularly in pediatric populations. However, the study acknowledged limitations, including the lack of tissue histological examinations, which could provide deeper insights into the therapeutic effects of the nanoemulsion. Future research is recommended to explore the application of this nano-formulation in clinical settings, particularly for malnourished pediatric patients suffering from hyperammonemia. In conclusion, the integration of nanotechnology in drug formulations represents a promising frontier in enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of nutraceuticals like curcumin and resveratrol, addressing significant medical challenges associated with hyperammonemia.
Reference
Nasr, Maha, Omar AH Ahmed-Farid, and Rania F. Ahmed. “Curcumin-resveratrol nano-formulation counteracting hyperammonemia in rats.” Metabolic Brain Disease 38.4 (2023): 1365-1377.
